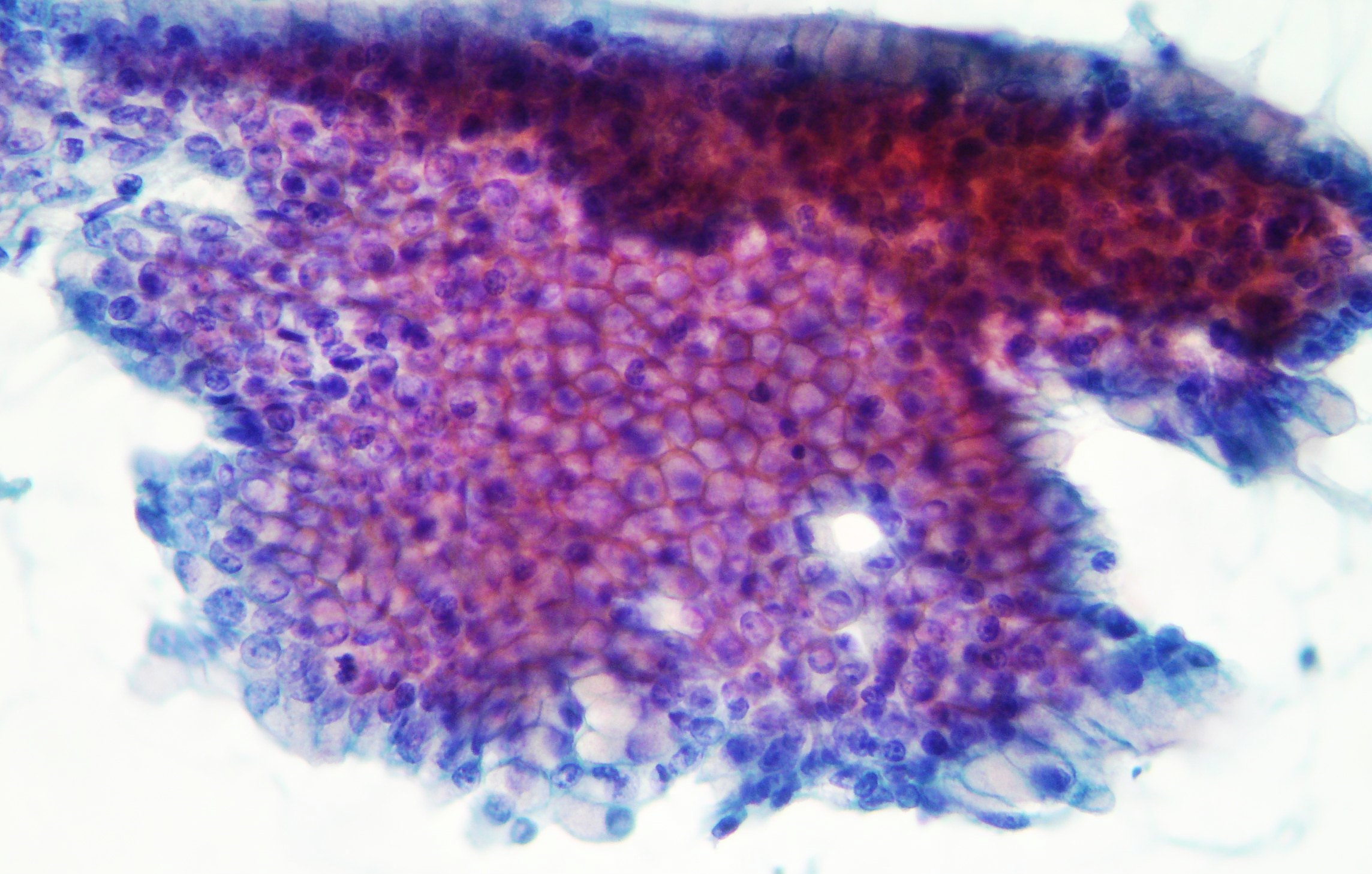
Lung metastasis of mucinous adenocarcinoma of the pancreas
A case of metastasis of mucinous well differentiated adenocarcinoma of the pancreas showing aggregates of neoplastic cells and mucoid background (Papanicolaou x200,x400)
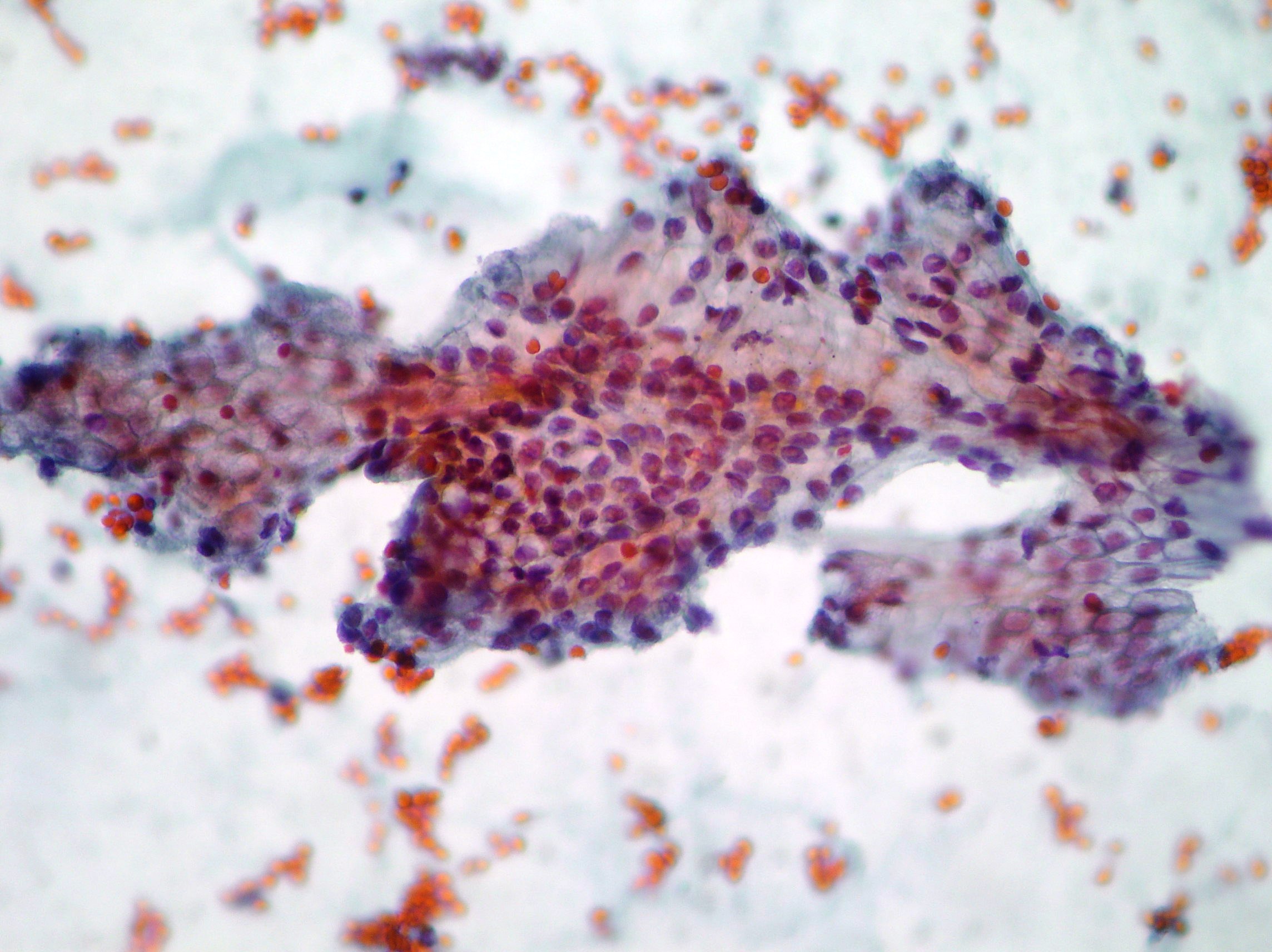
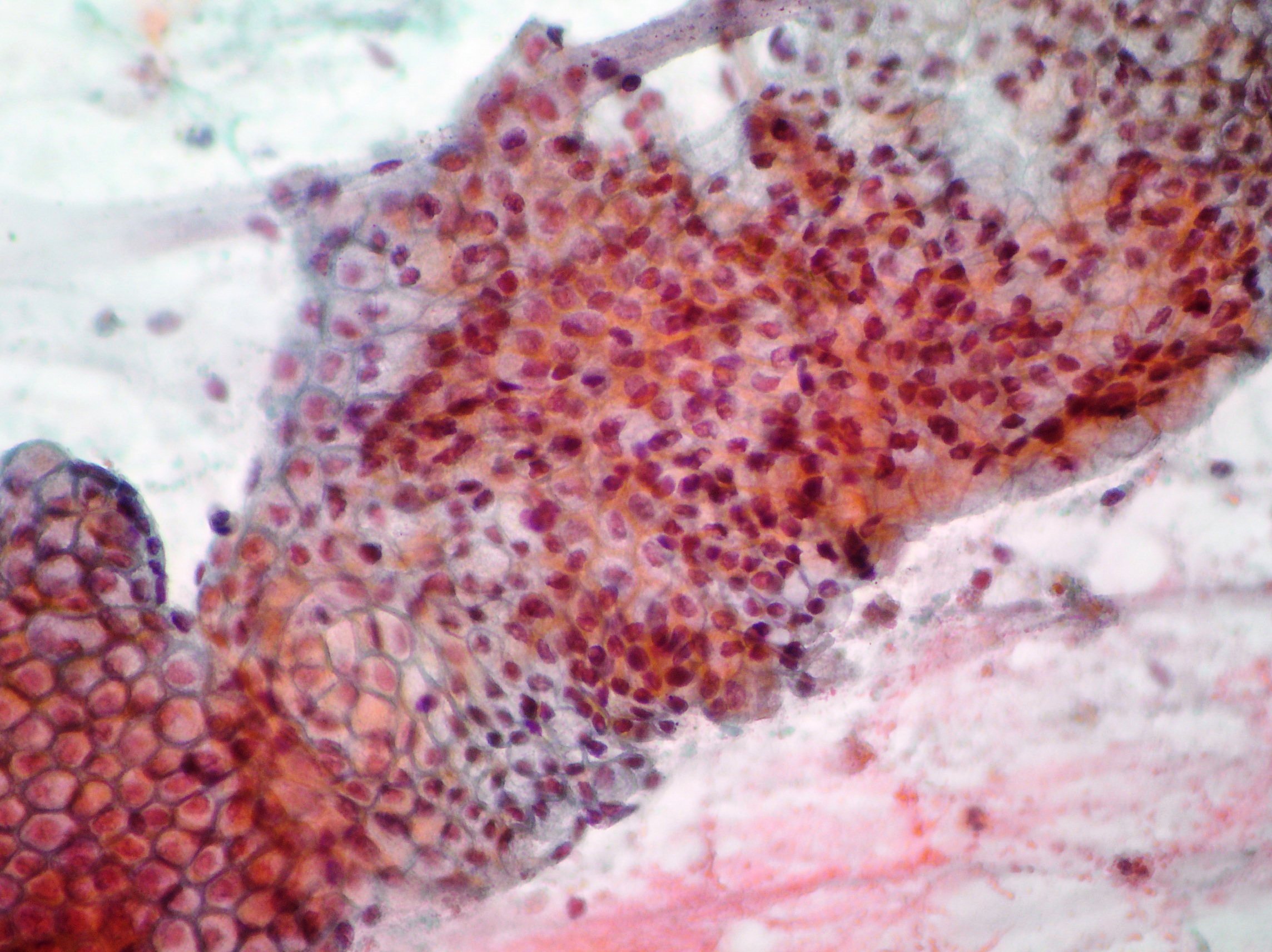
Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Groups and aggregates of adenocarcinoma cells obtained after gastric washing (Papanicolaou x200,x400)
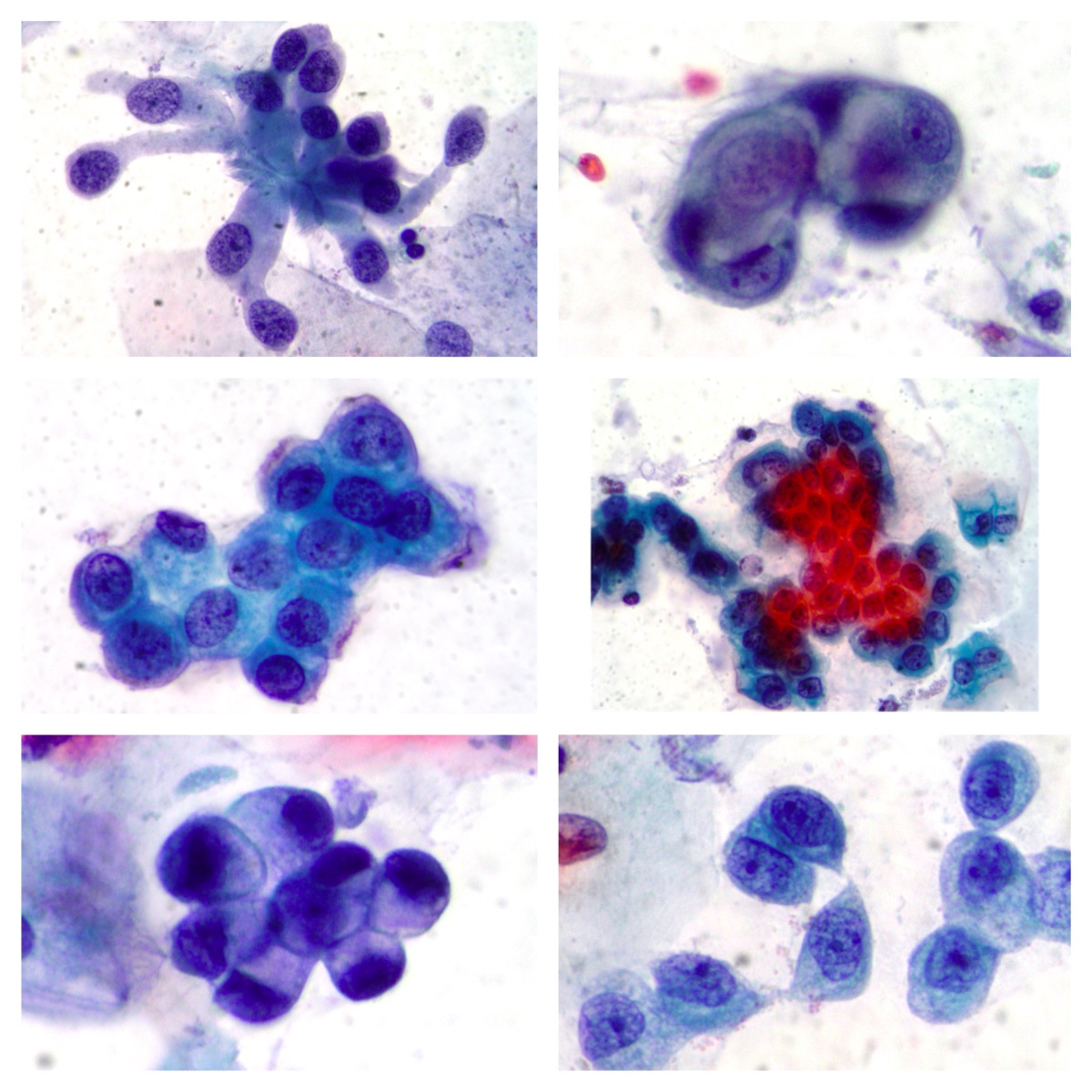
CPRE. Cholangiocarcinoma
Neoplastic cells from a case of cholangiocarcinoma (Papanicolaou x200,x400).
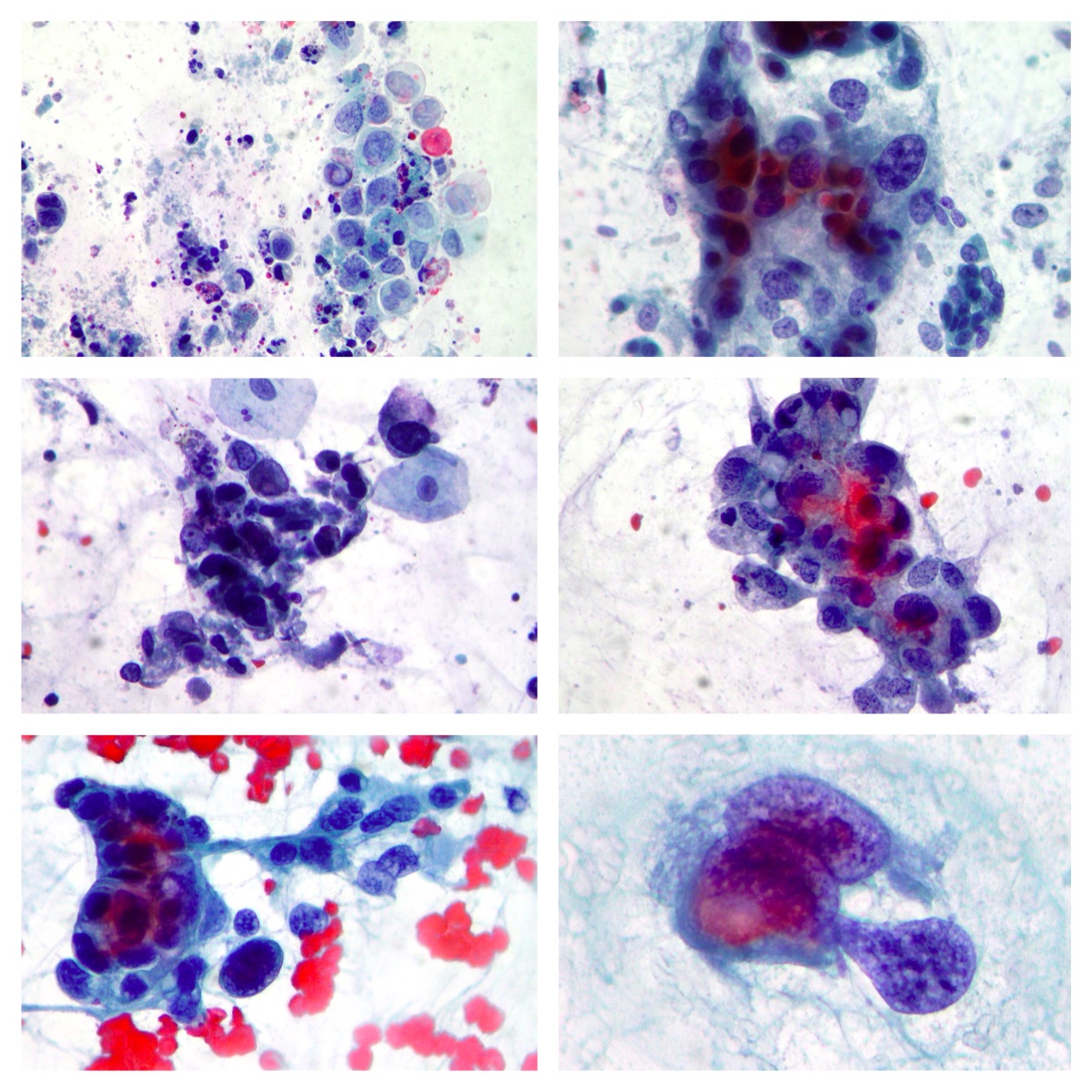
EUS-FNA. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Clusters of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells showing abnormalities such as nuclear enlargement and coarse chromatin(Papanicolaou x200, Diff-Quik stain)
EUS-FNA. Pancreatic Endocrine Tumor.
Relatively monotonous sometimes round to polygonal neoplastic cells arranged singly or in clusters suggestive of endocrine tumor(Papanicolaou x100, x200)
EUS-FNA. Pancreatic Adenosquamous Carcinoma.
Markedly atypical clusters and isolated glandular and squamous cells associated to debris and inflammatory cells on the background. (Papanicolaou x100, 200)
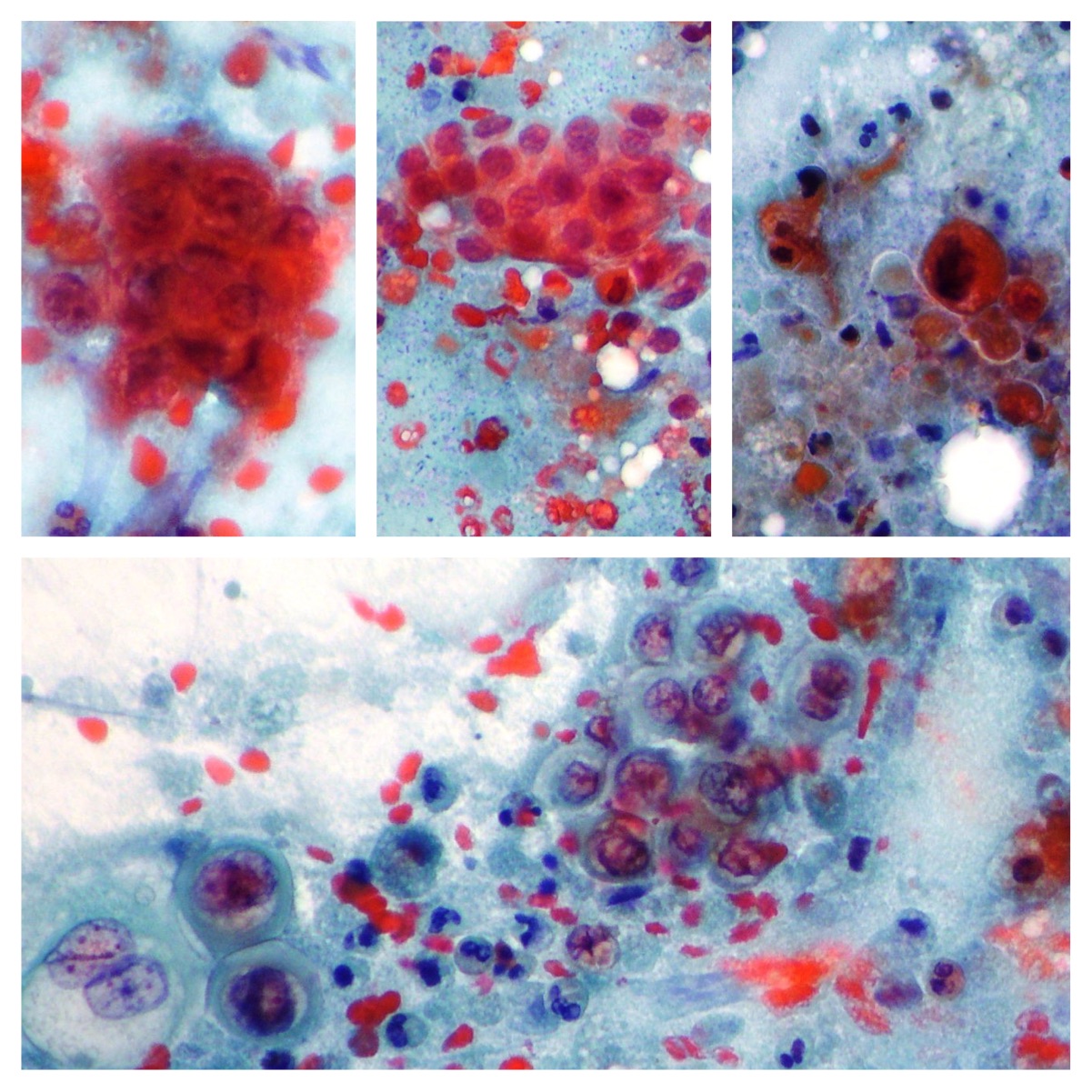
EUS-FNA. Pancreatic Endocrine Tumor
A case of pancreatic endocrine tumor showing basophilic cytoplasm, nuclear pleomorphism, multi nucleation and prominent nucleoli. Endocrine diagnosis was supported by immunohistochemistry (Papanicolaou x200)
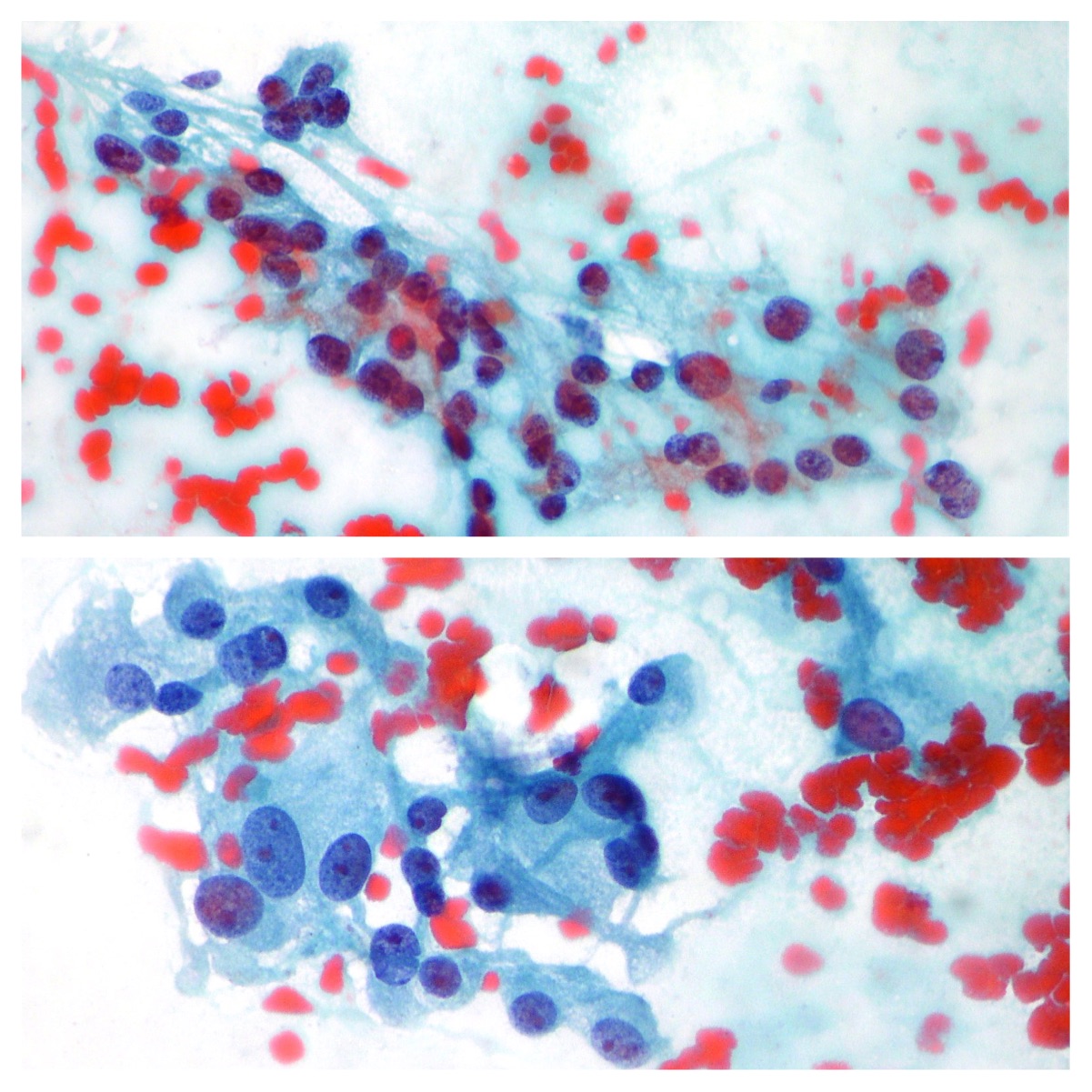
Liver FNAB. Liver metastasis of neuroendocrine tumor.
Liver FNAB. Liver metastasis of neuroendocrine tumor (on the right side). Left side of the picture is characterized by normal hepatocytes. (Papanicolaou x200)
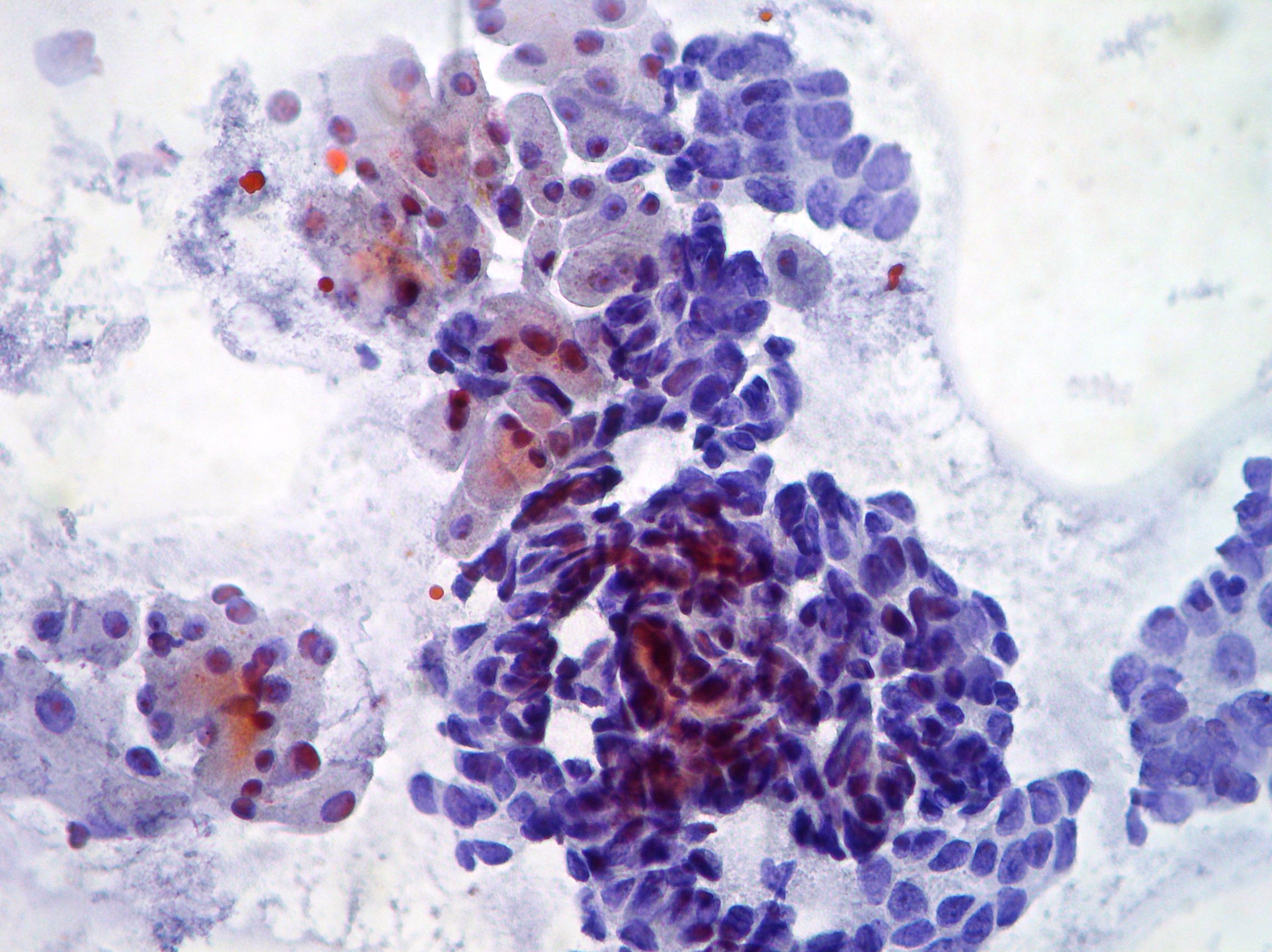
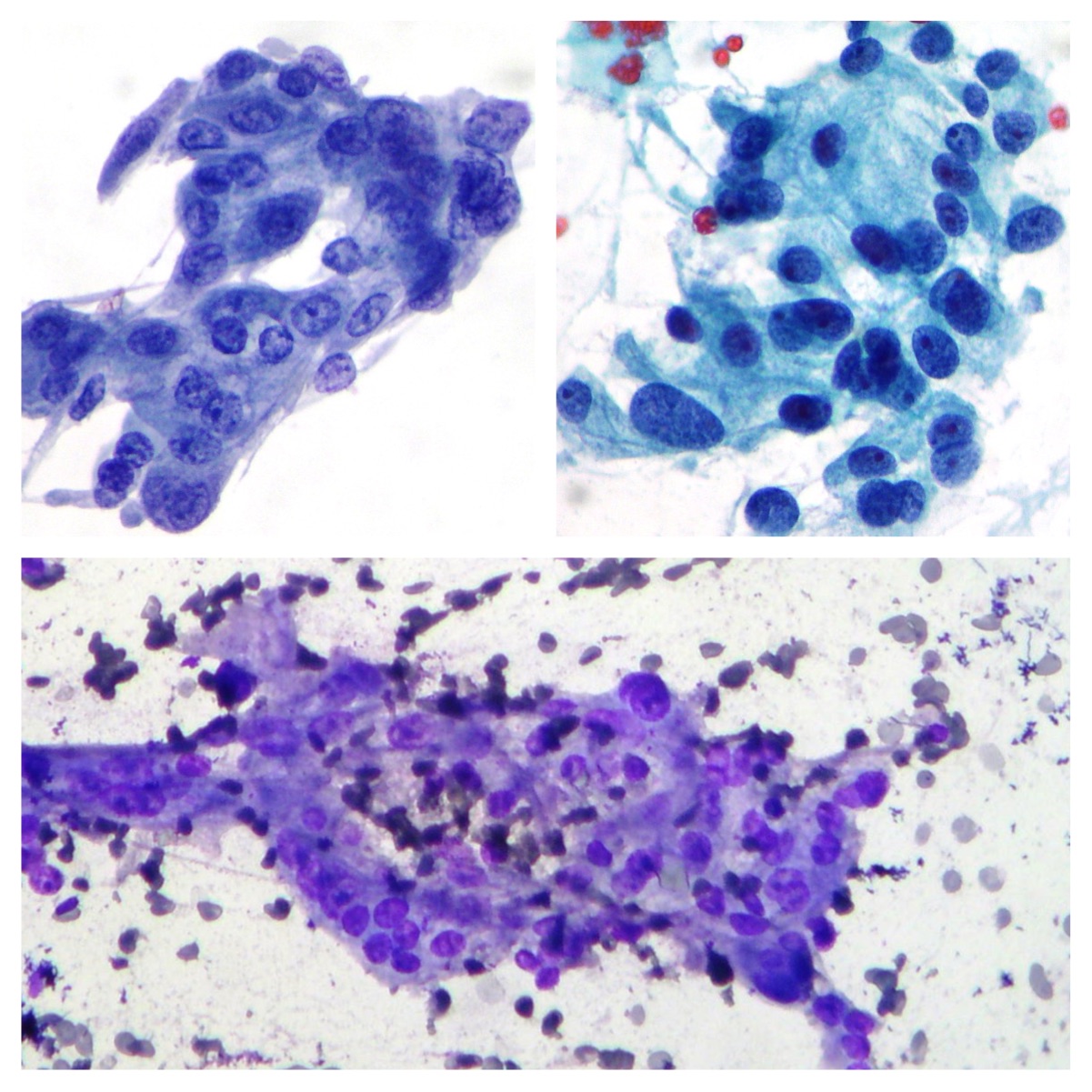
Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas
Single and large neoplastic multinucleated cells suggestive of osteoclastic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (Papanicolaou x200)
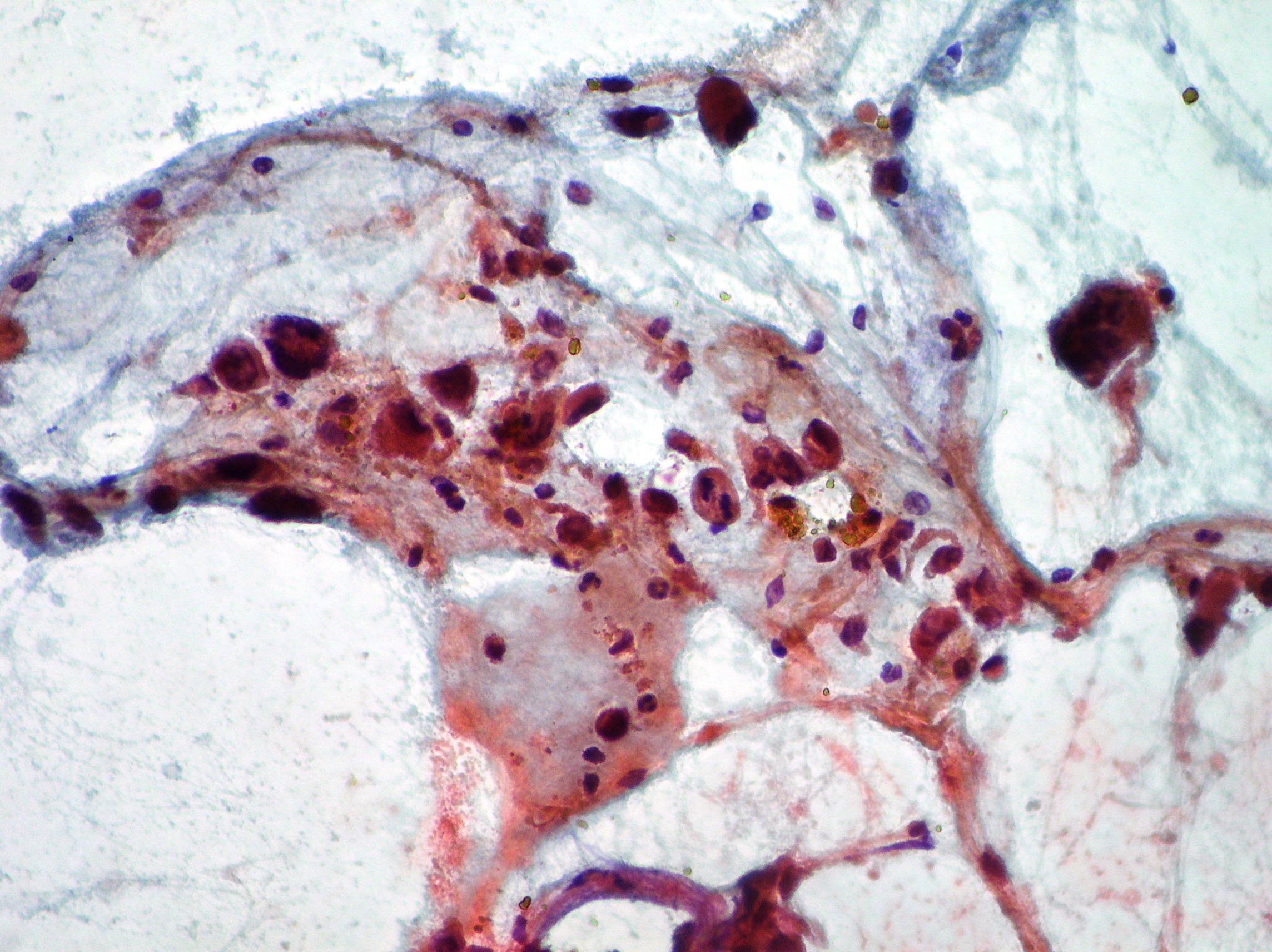
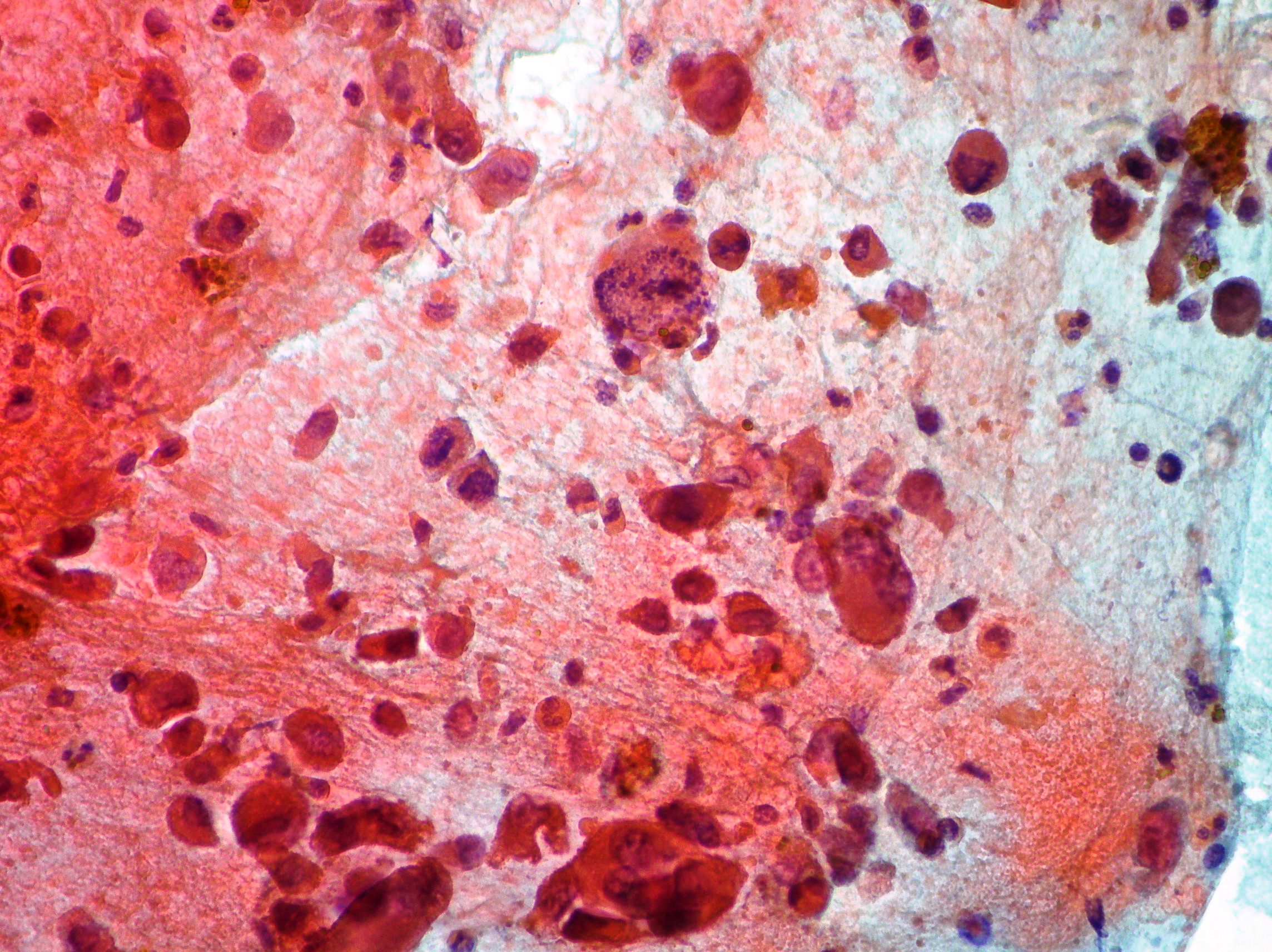
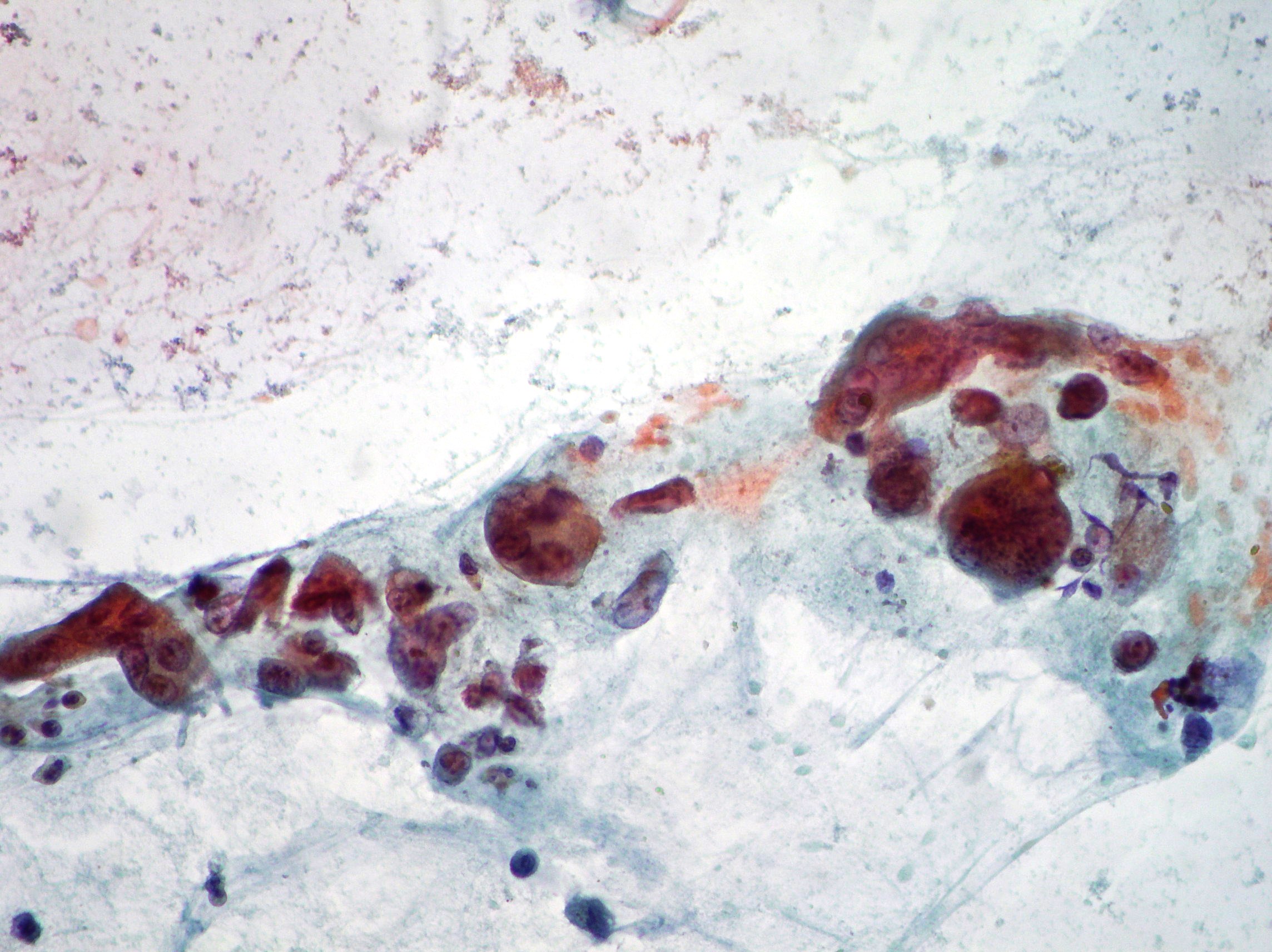
CPRE. Cholangiocarcinoma
Neoplastic cells from a case of cholangiocarcinoma (Papanicolaou x200, x100, x200).
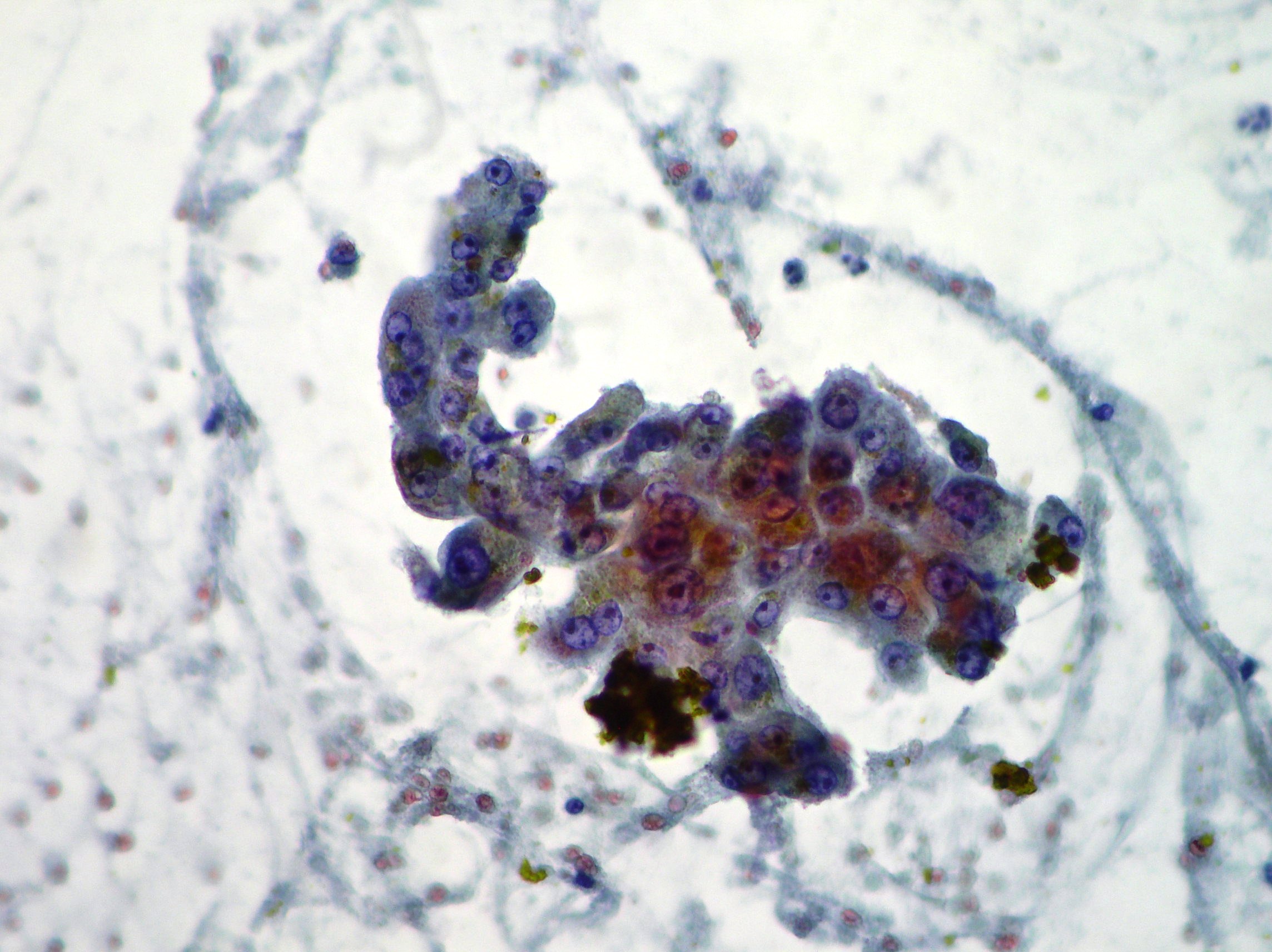
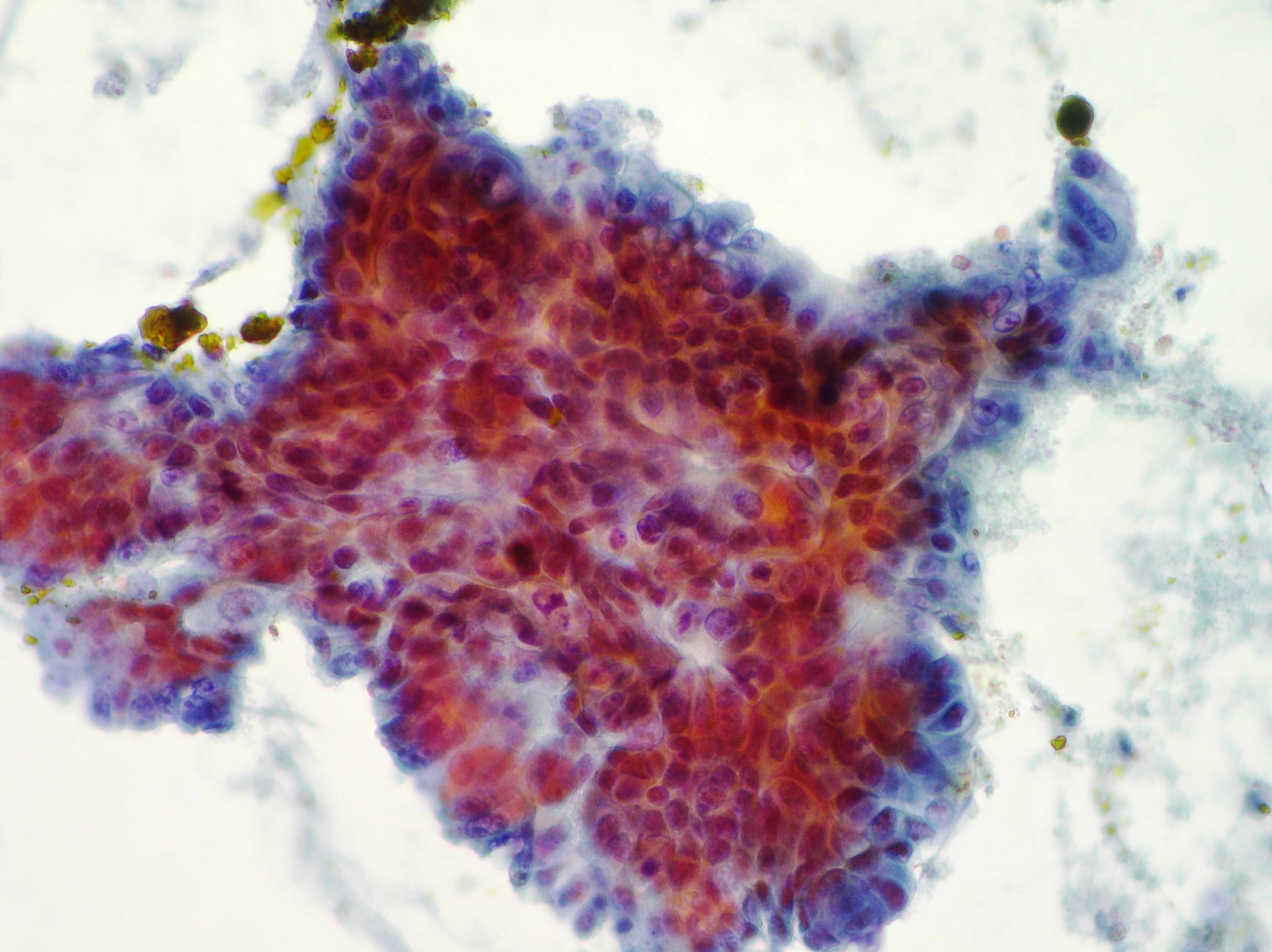
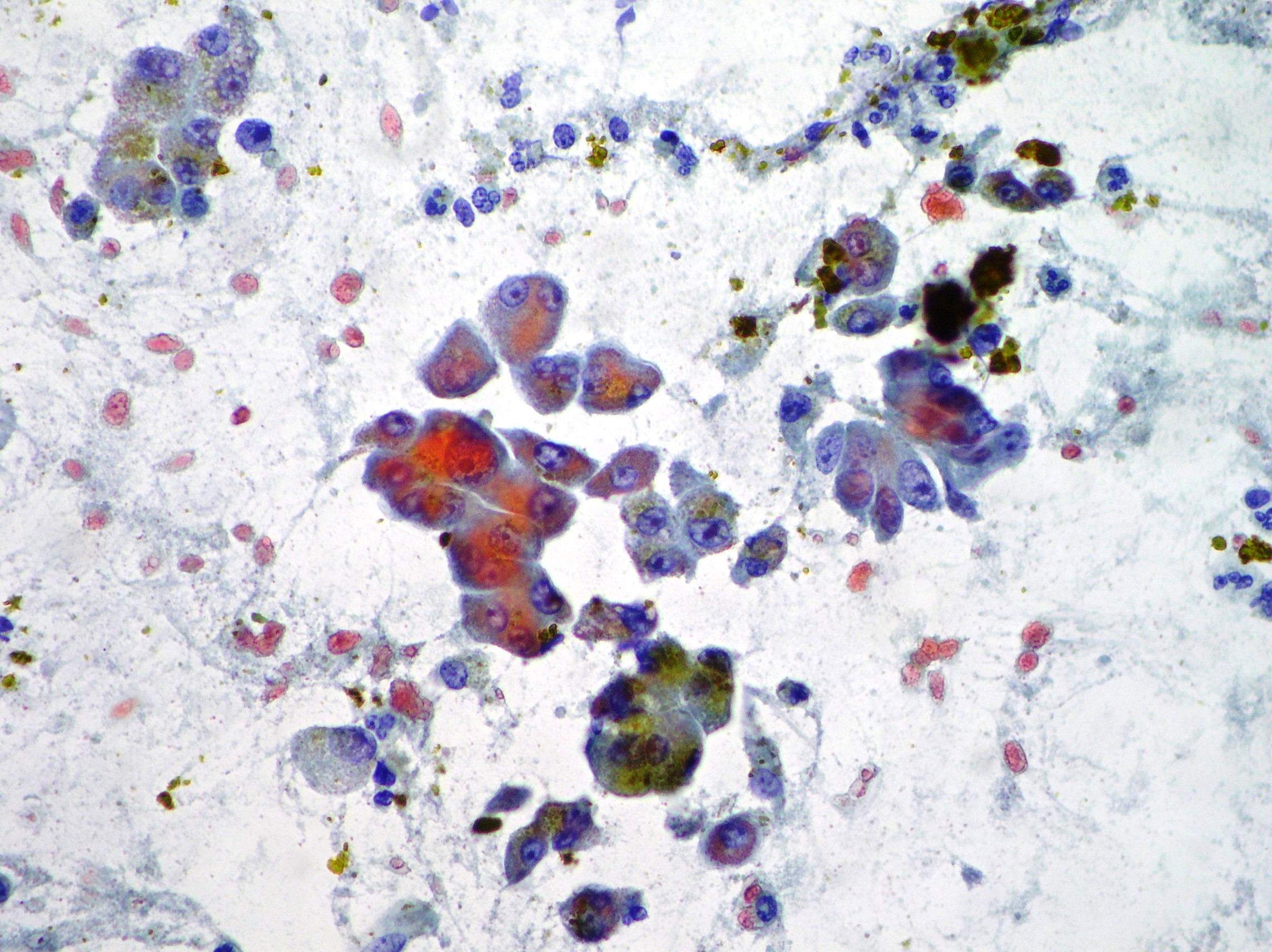
Anaplastic pancreatic carcinoma
Anaplastic pancreatic carcinoma showing pleomorphic, mononuclear and multinucleate neoplastic cells (Papanicolaou x200).
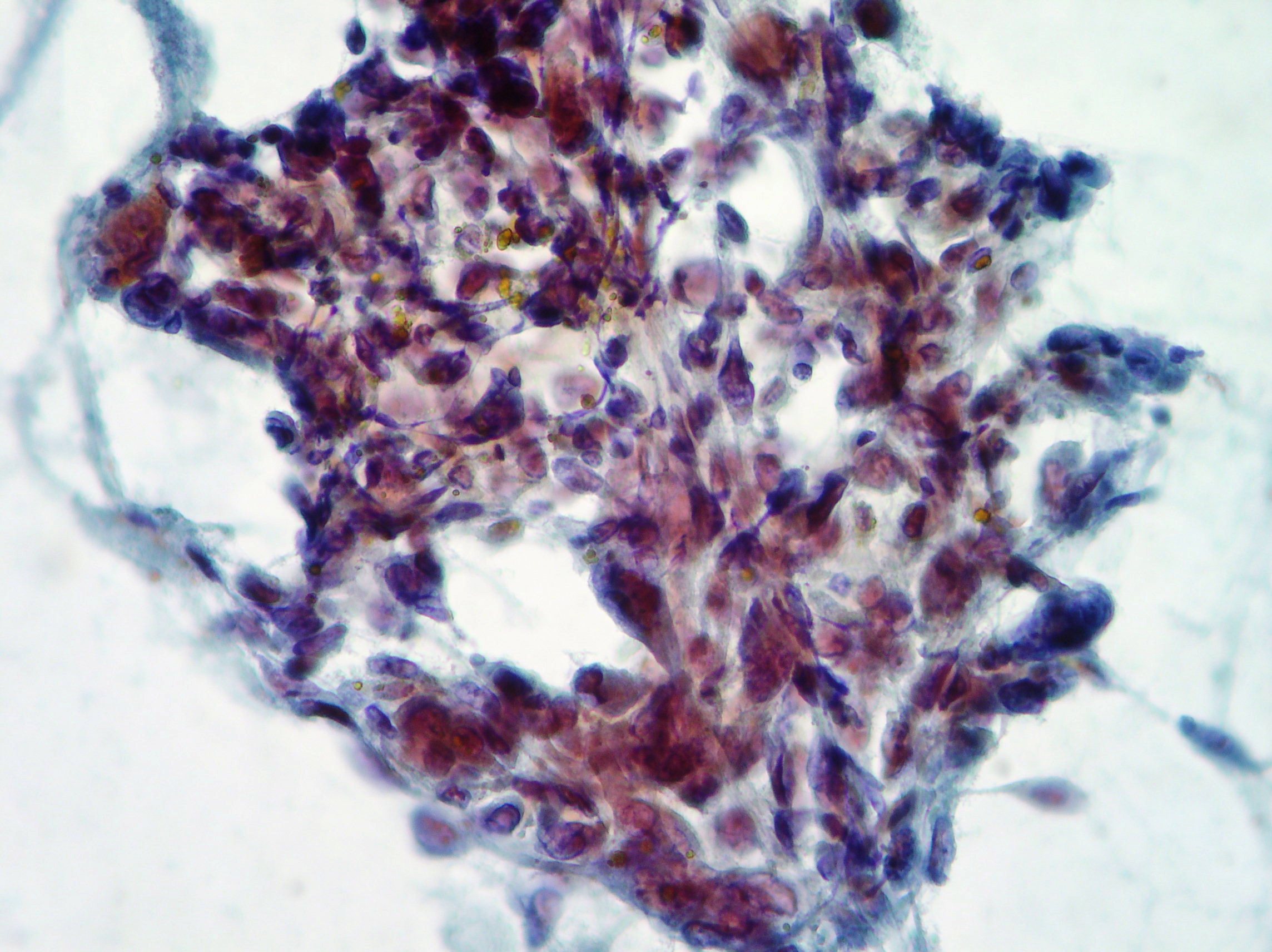
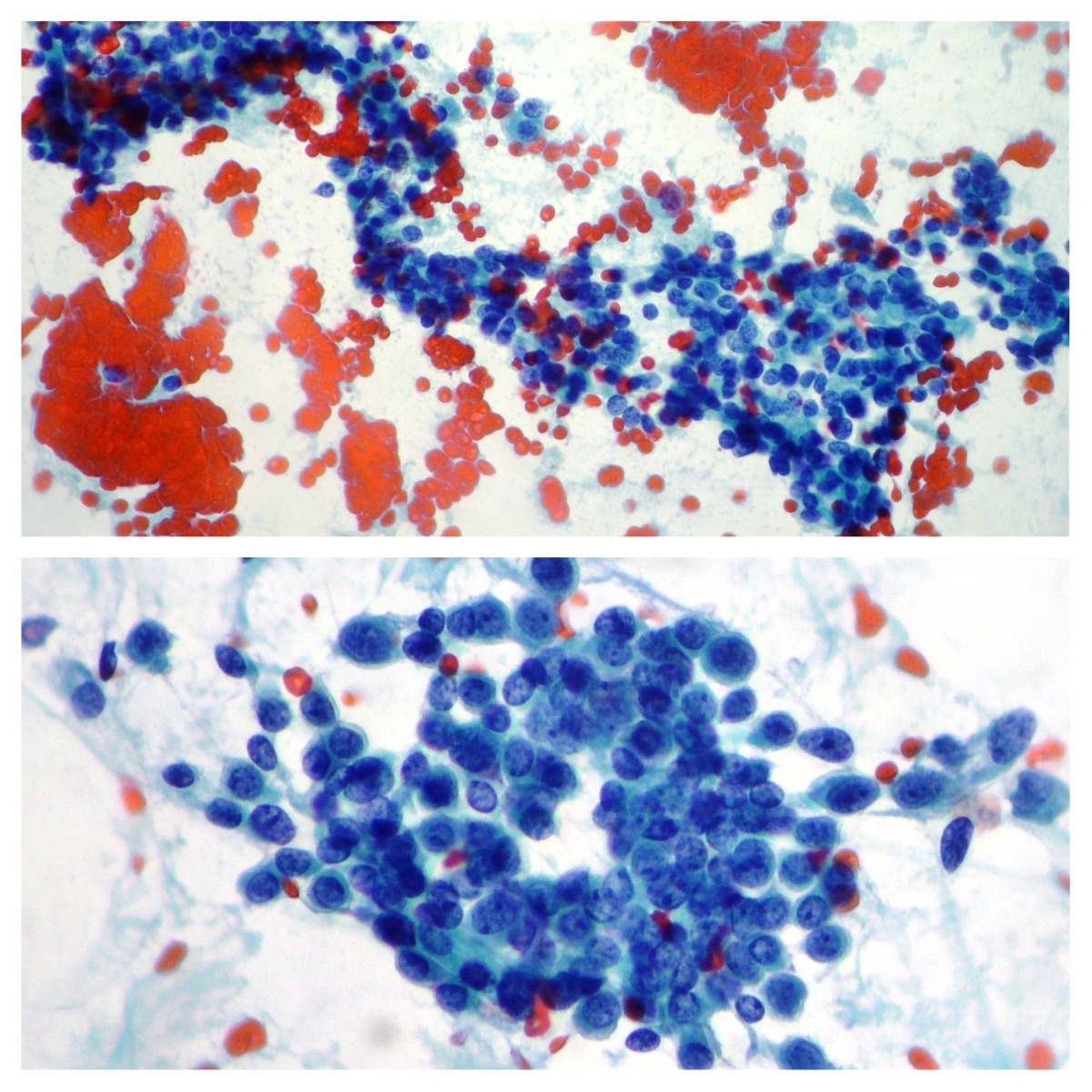
Normal hepatocytes
Normal hepatocytes showing intra cytoplasmic granular pigments, round and regular nuclei with prominent nucleoli (Papanicolaou x400)
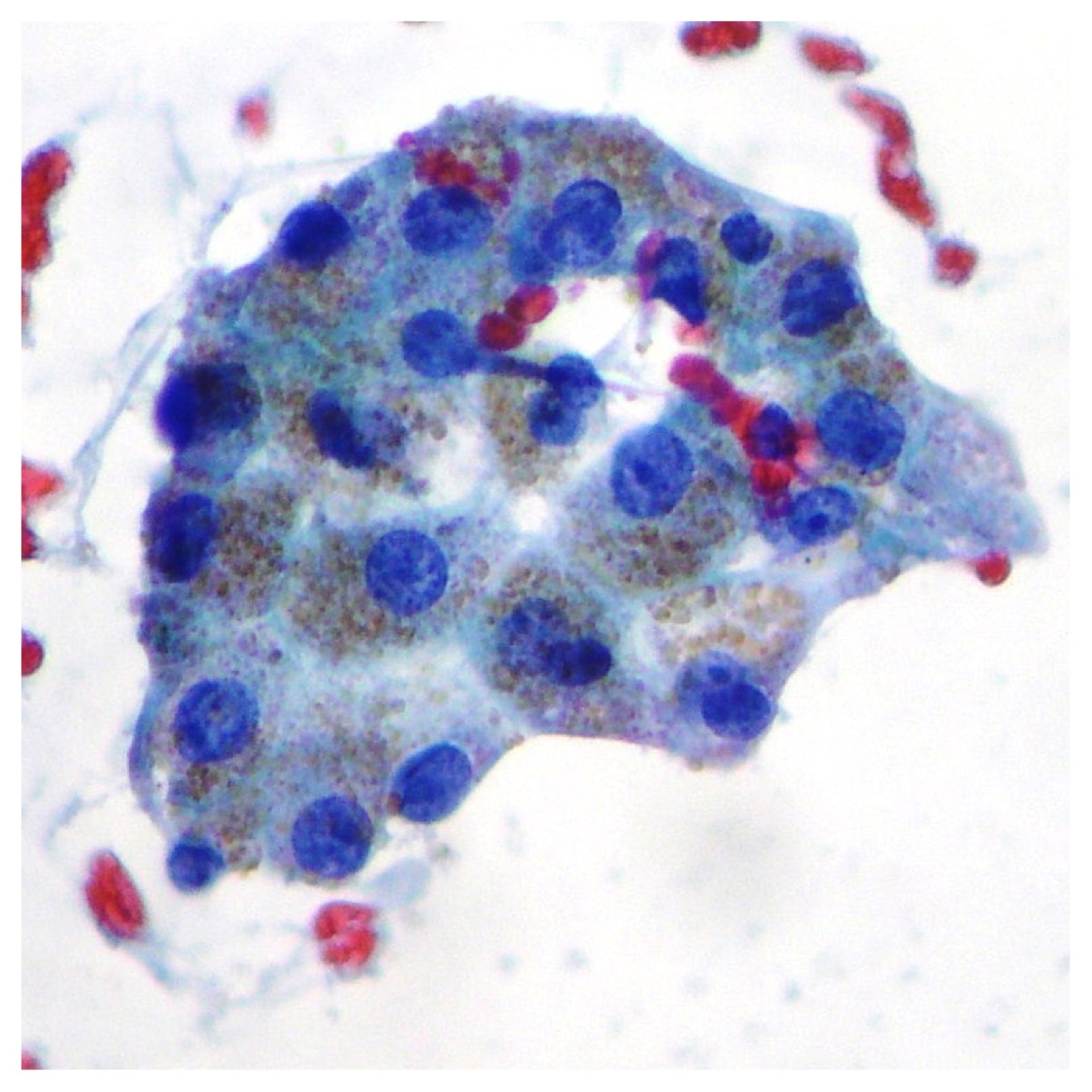
Normal pancreatic glandular cells
Normal pancreatic glandular cells obtained after Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (CPRE) (Papanicolaou x100, x200)
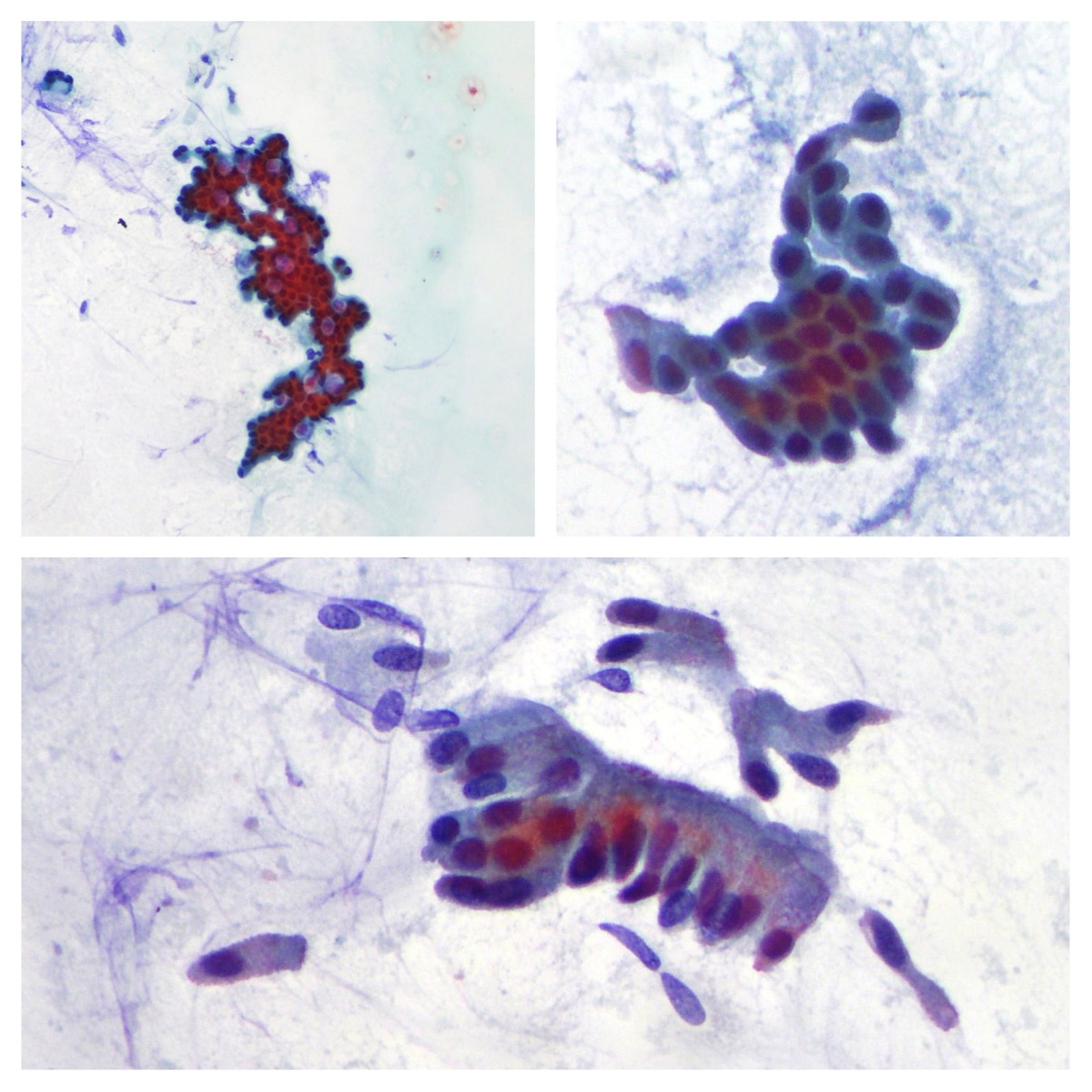
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma presenting cohesive epithelial cells with nuclear crowding, overlapping, nuclear atypia and mitosis. (Papanicolaou x200, Rapid On Site Evaluation x100)
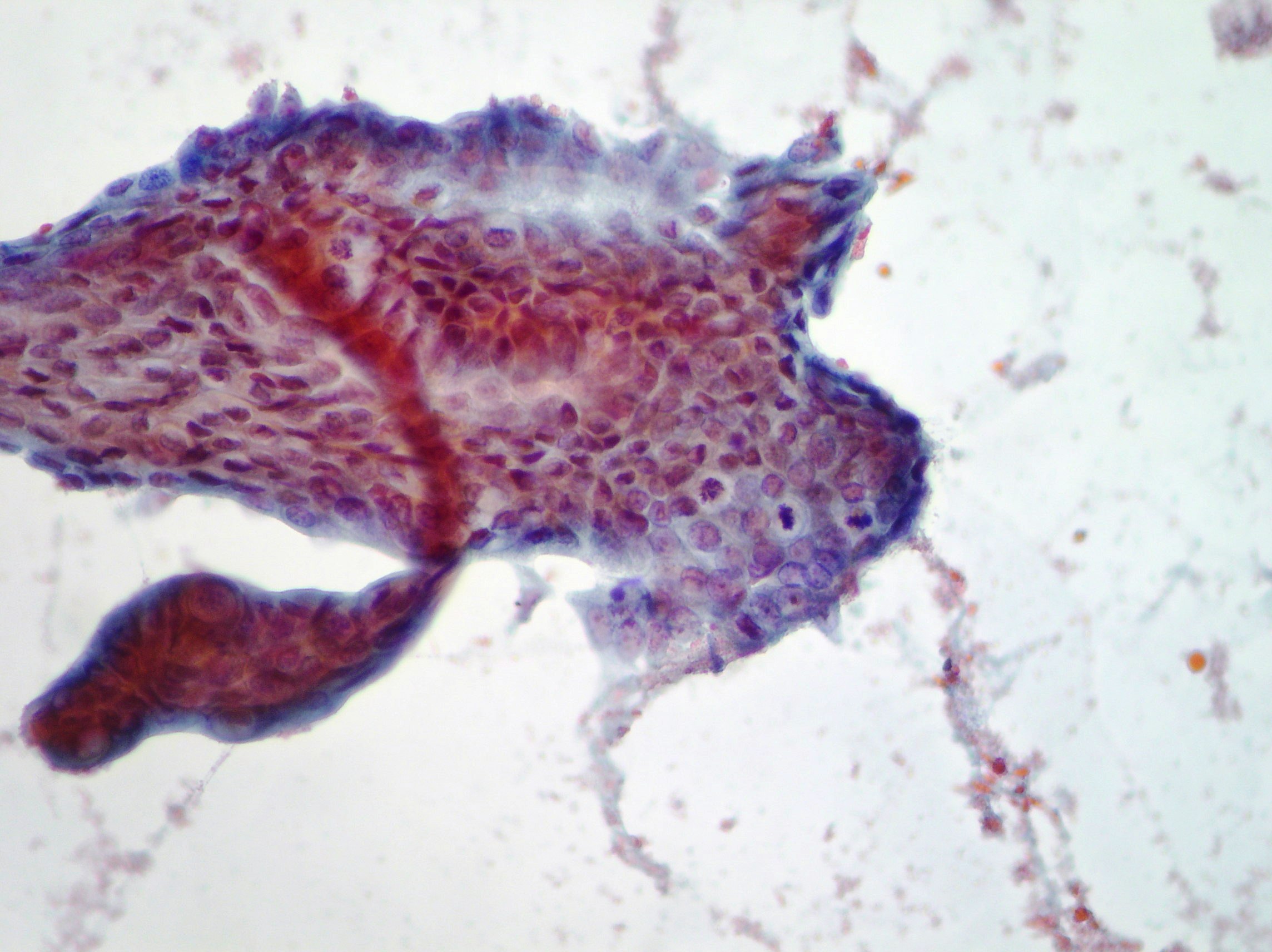
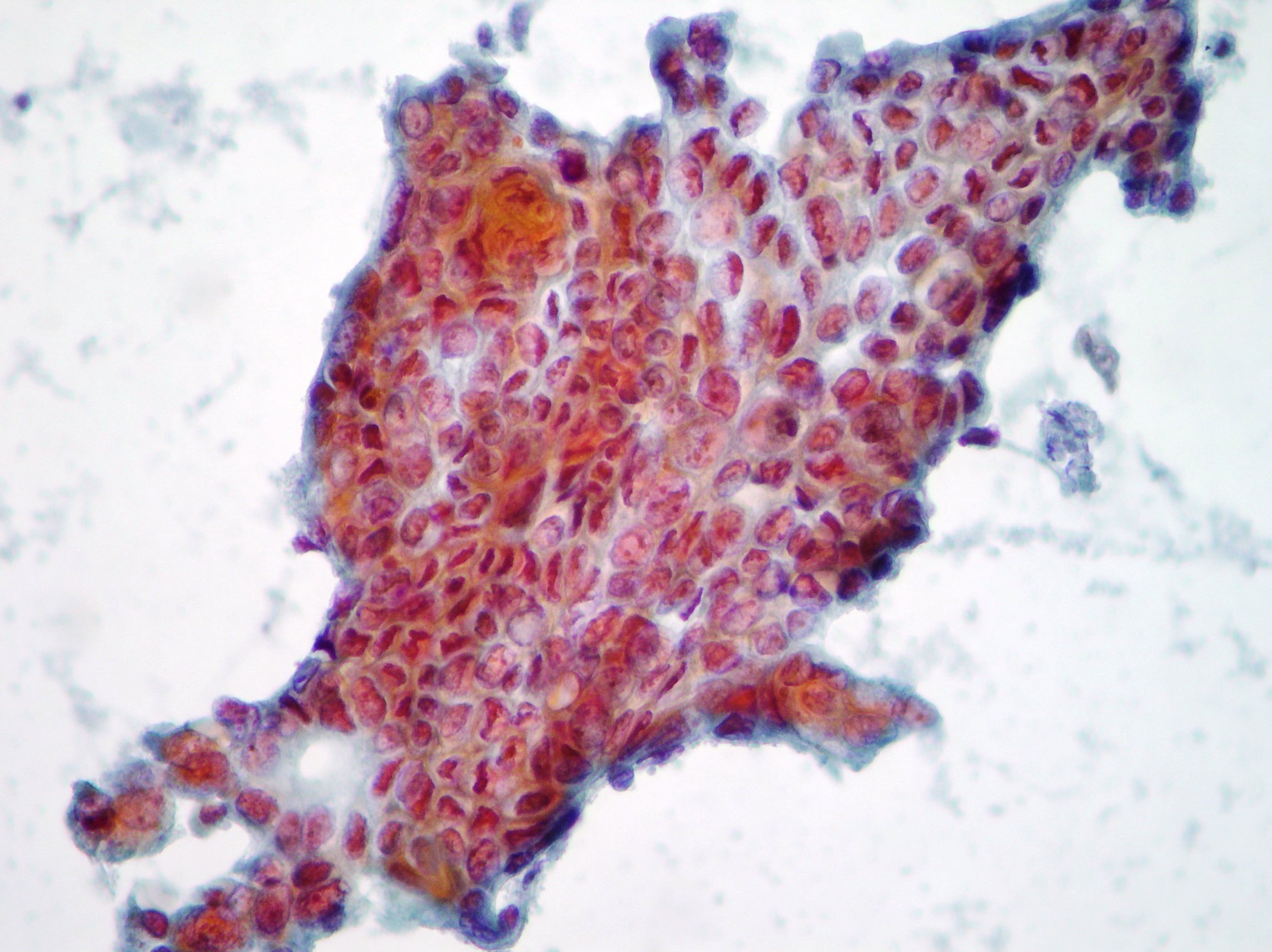
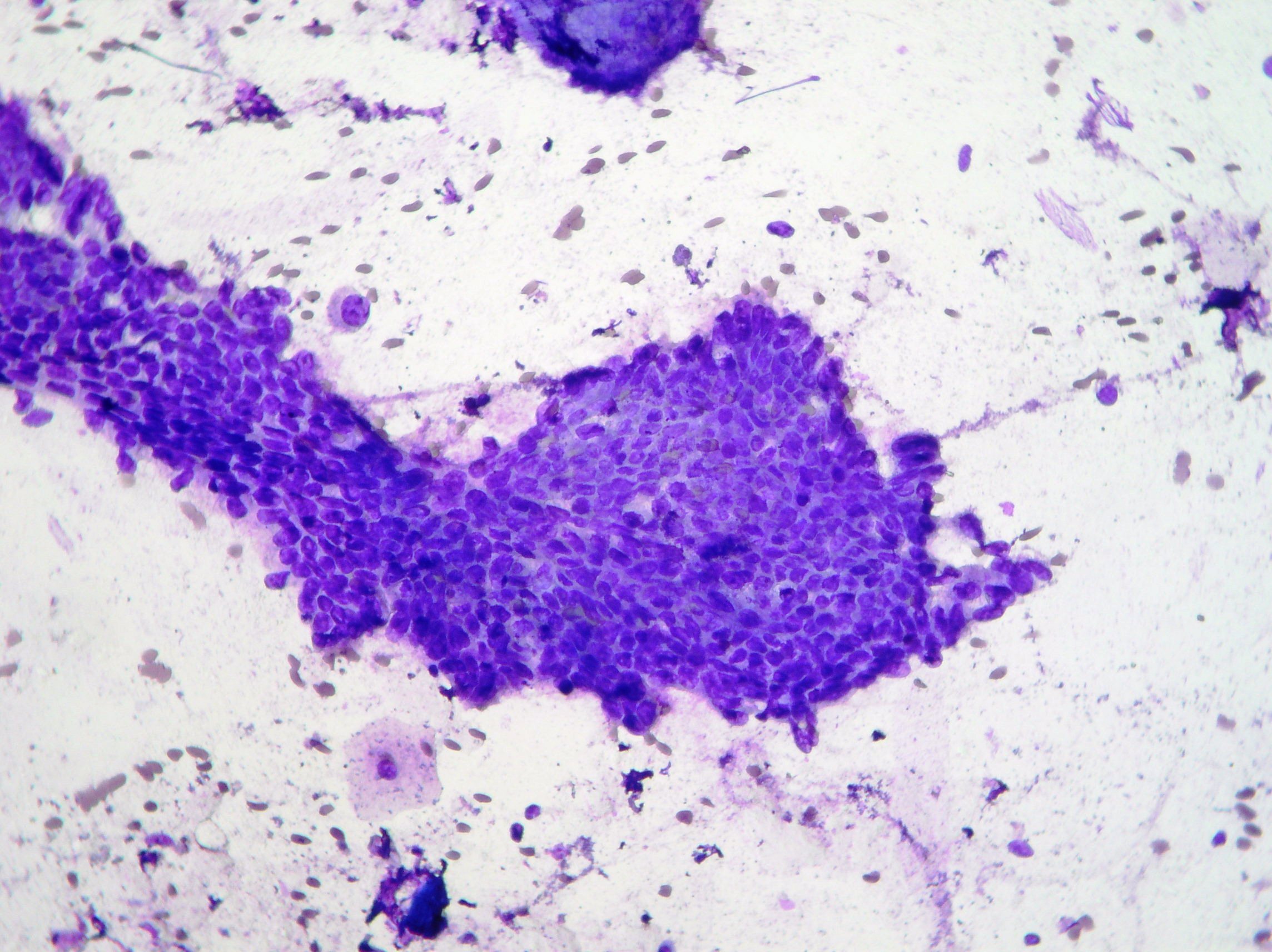
Liver metastasis
Liver metastasis of neuroendocrine tumor confirmed by immunohistochemistry on the biopsy. (Papanicolaou x100, x400)
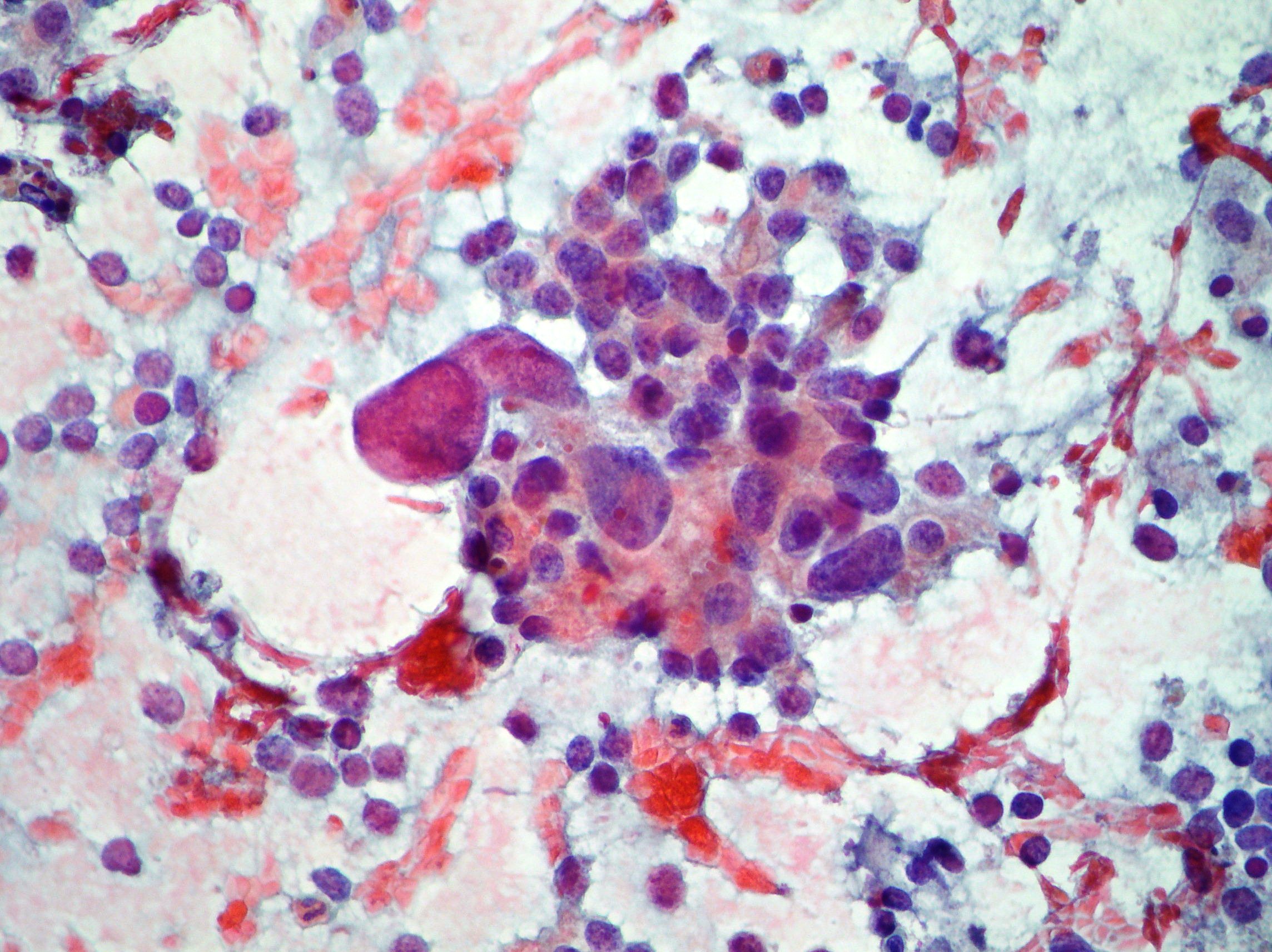
Neuroendocrine pancreatic carcinoma
Neuroendocrine pancreatic carcinoma showing dispersed population of cells with moderate anisokaryosis and fragile cytoplasm. Neuroendocrine CD 56 marker immunostaining resulted positive. (Papanicolaou, x200)
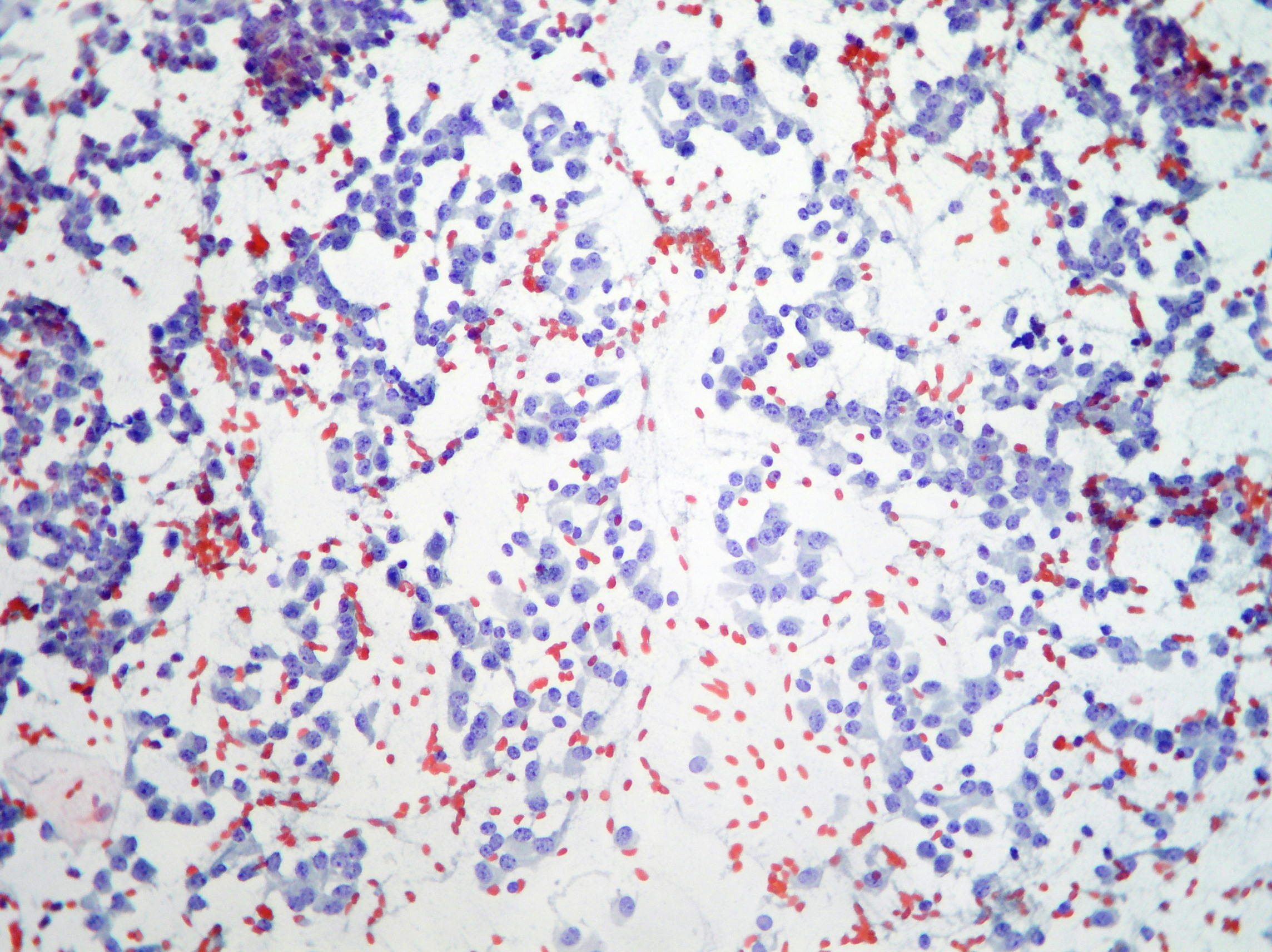
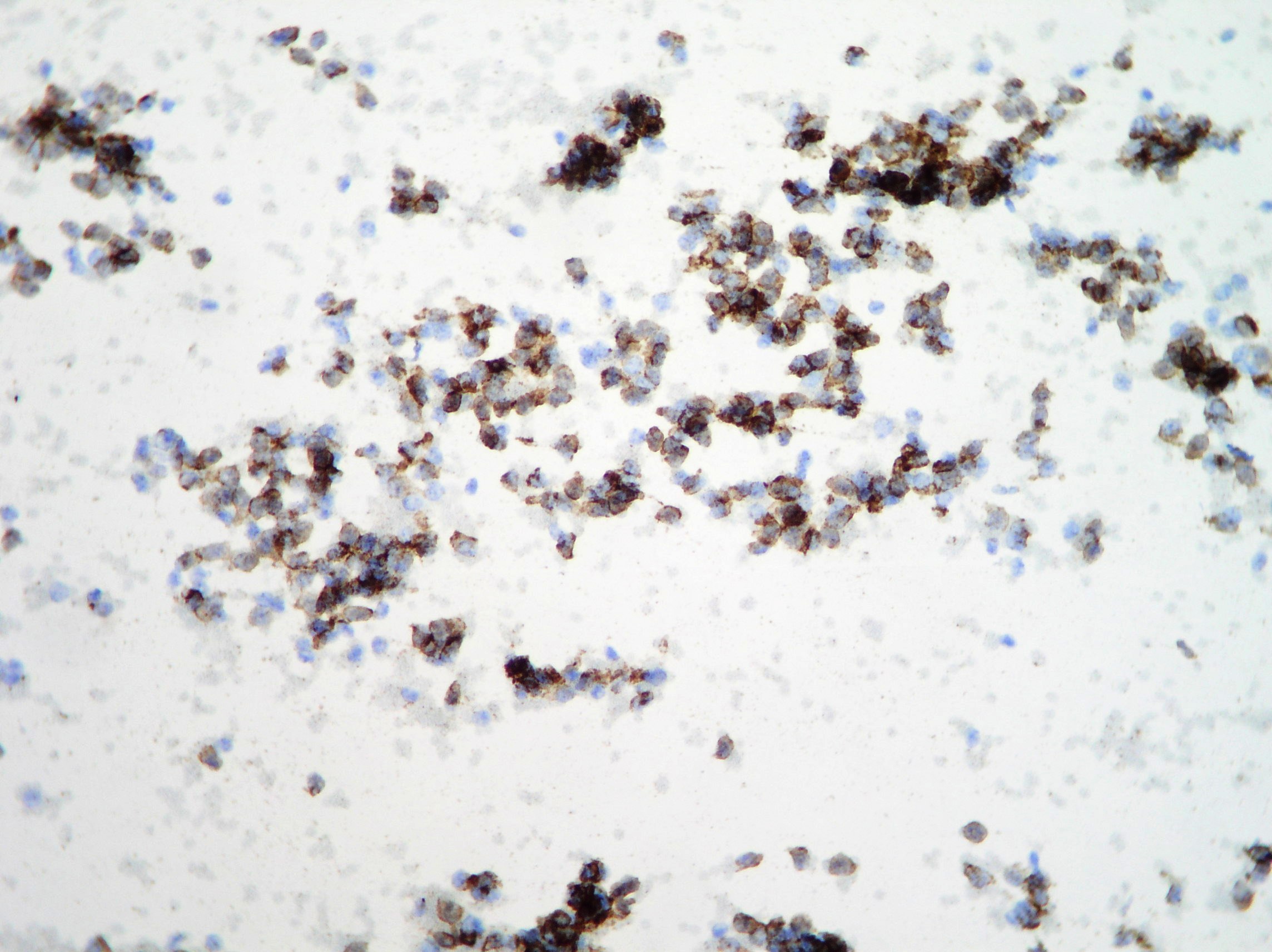
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Naked and large round nuclei with macro nucleoli suggestive of hepatocellular carcinoma. (Papanicolaou, x400)
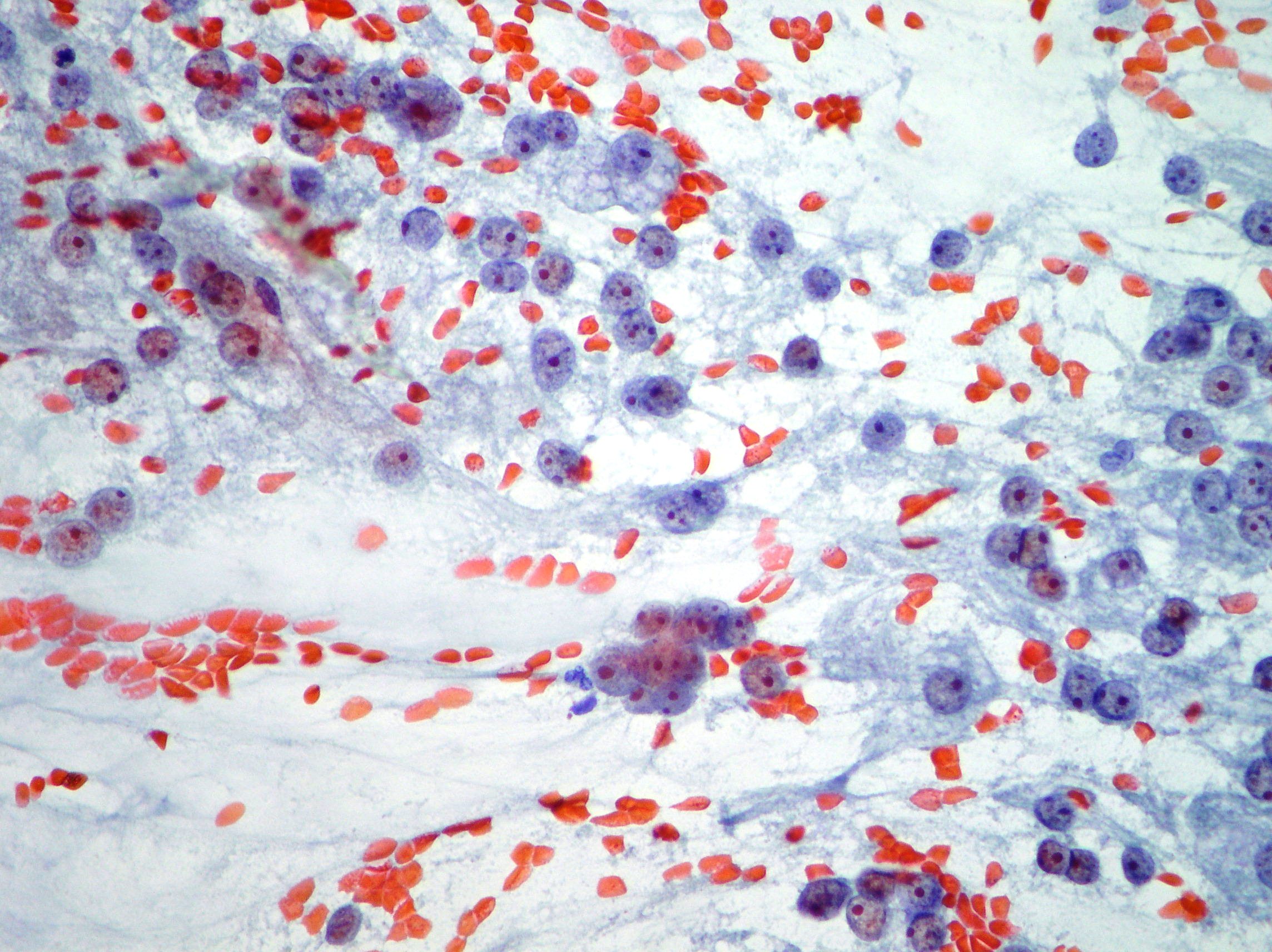
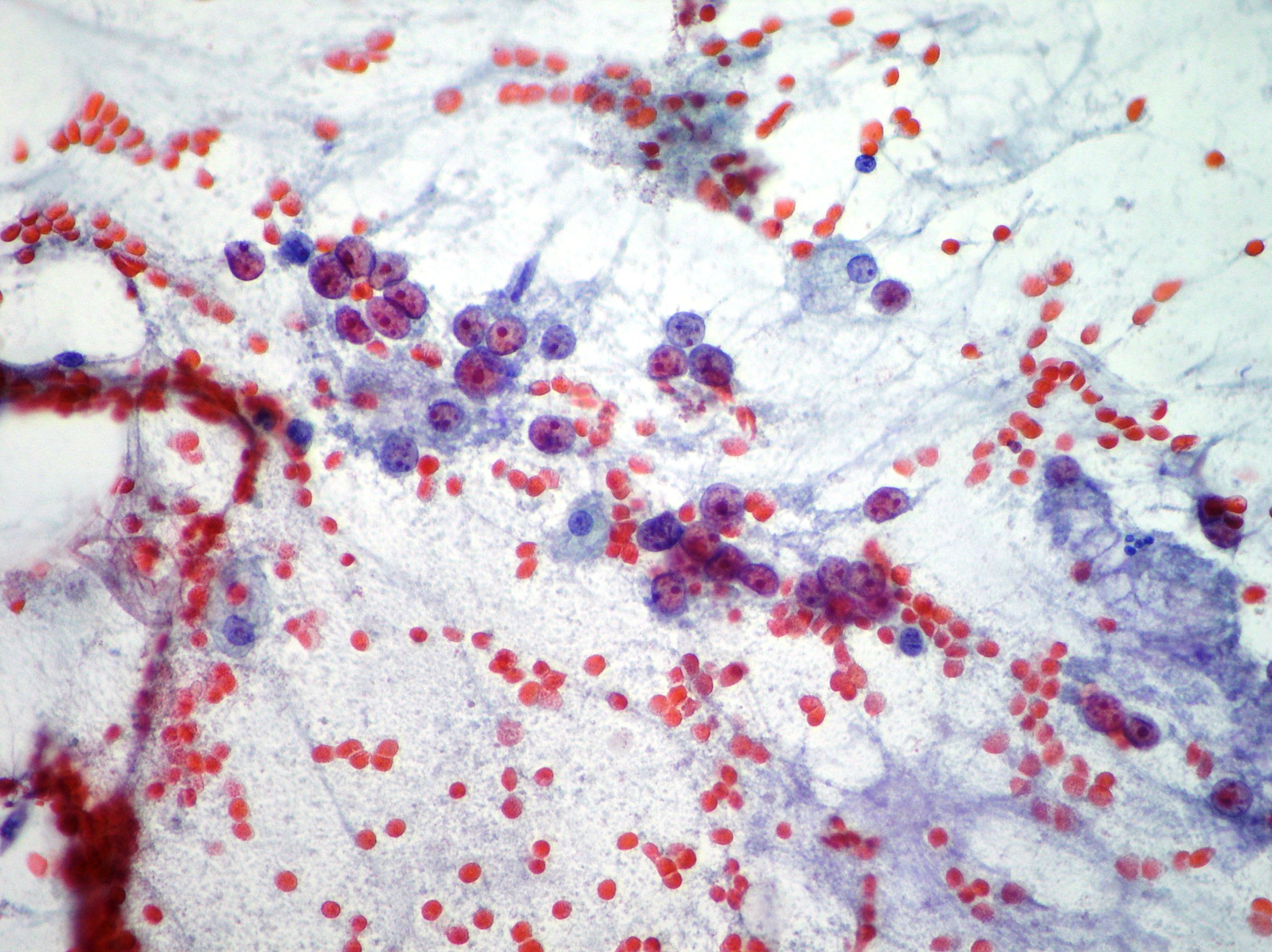
Mucinous pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Malignant epithelium showing pleomorphism and irregular nuclei suggestive of mucinous pancreatic adenocarcinoma. (Papanicolaou, x400)
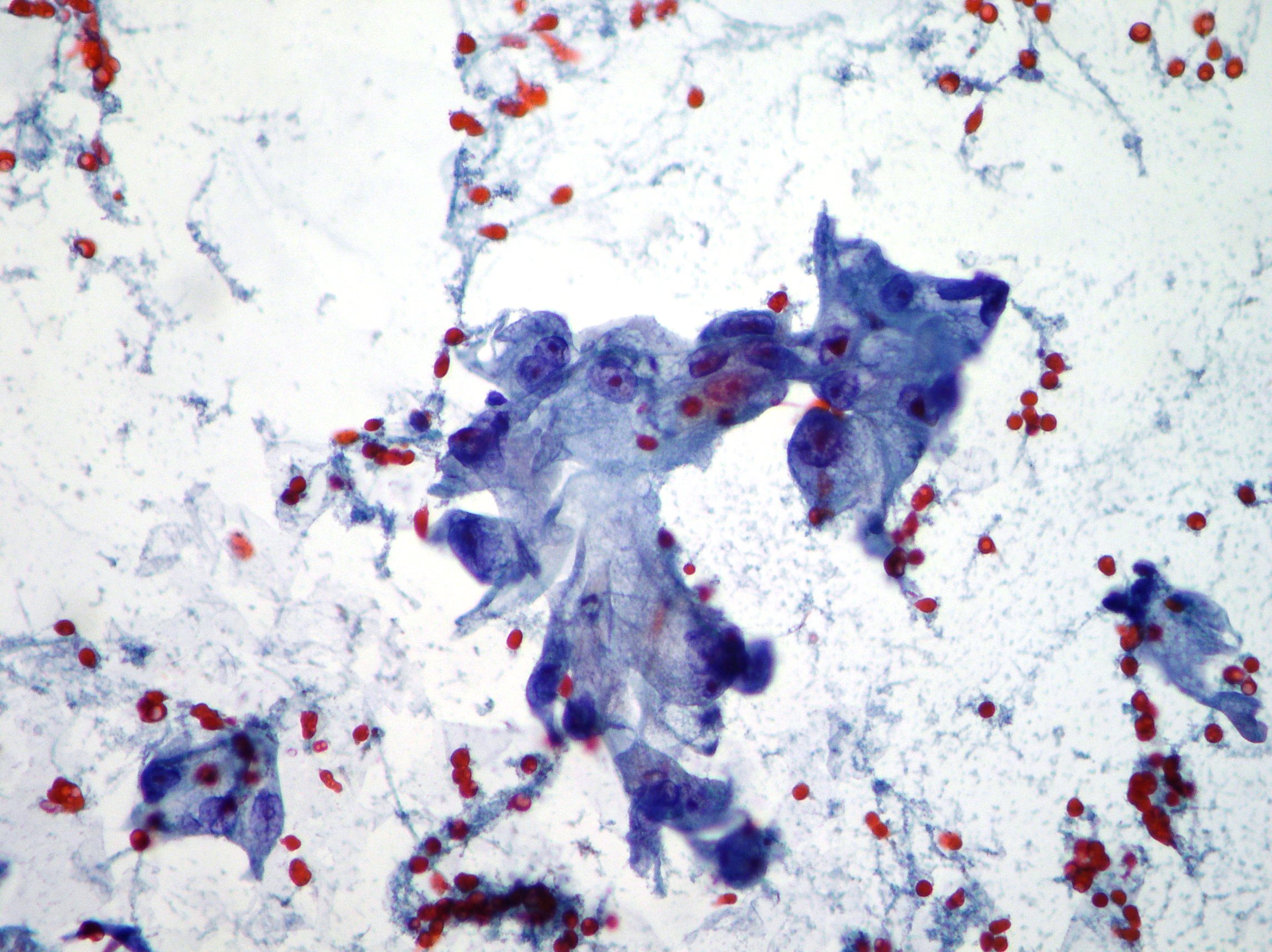
Pancreatic neoplasia
Atypical epithelium showing pleomorphism and irregular nuclei suggestive of pancreatic neoplasia. (Papanicolaou, x400)
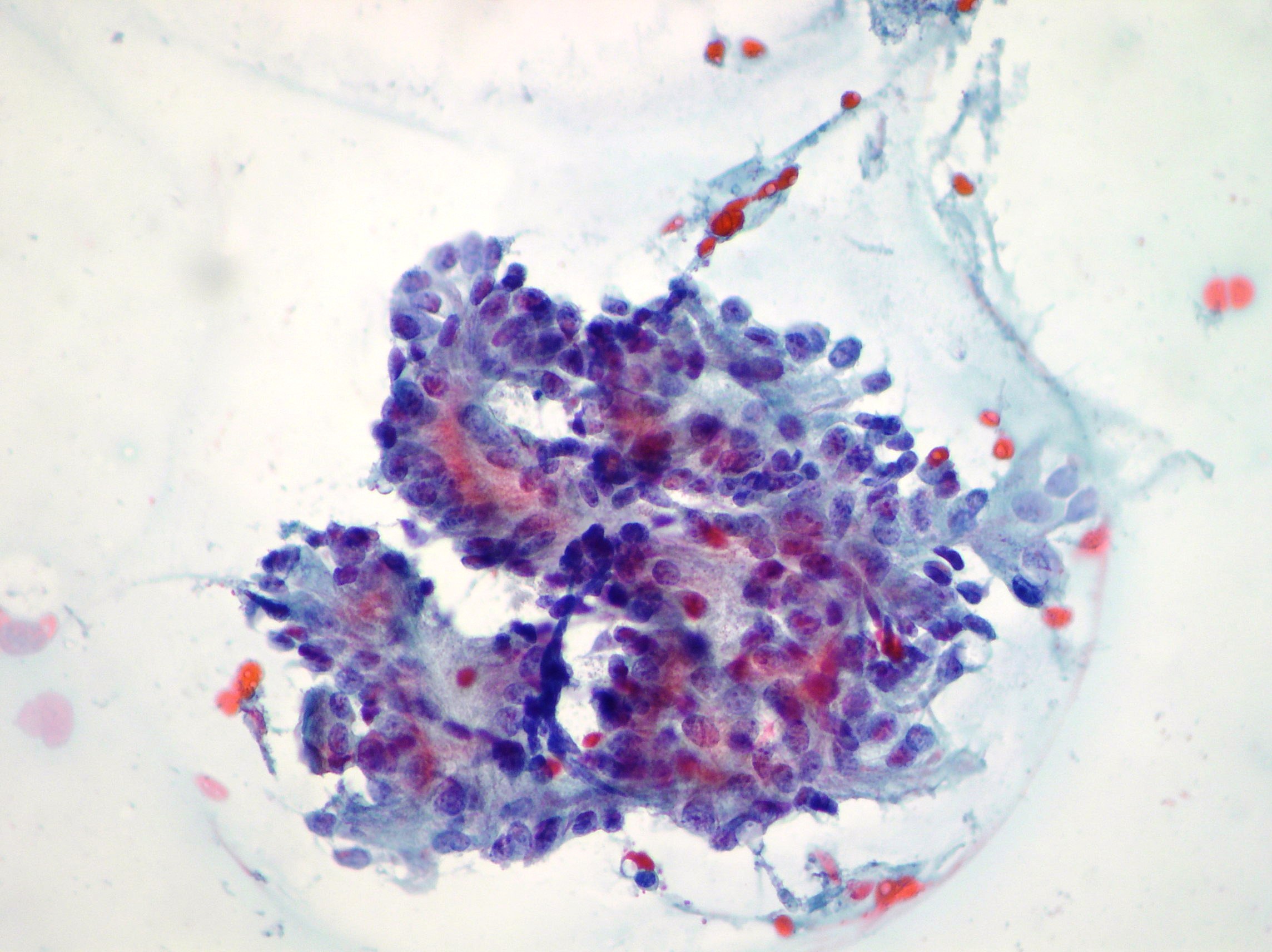
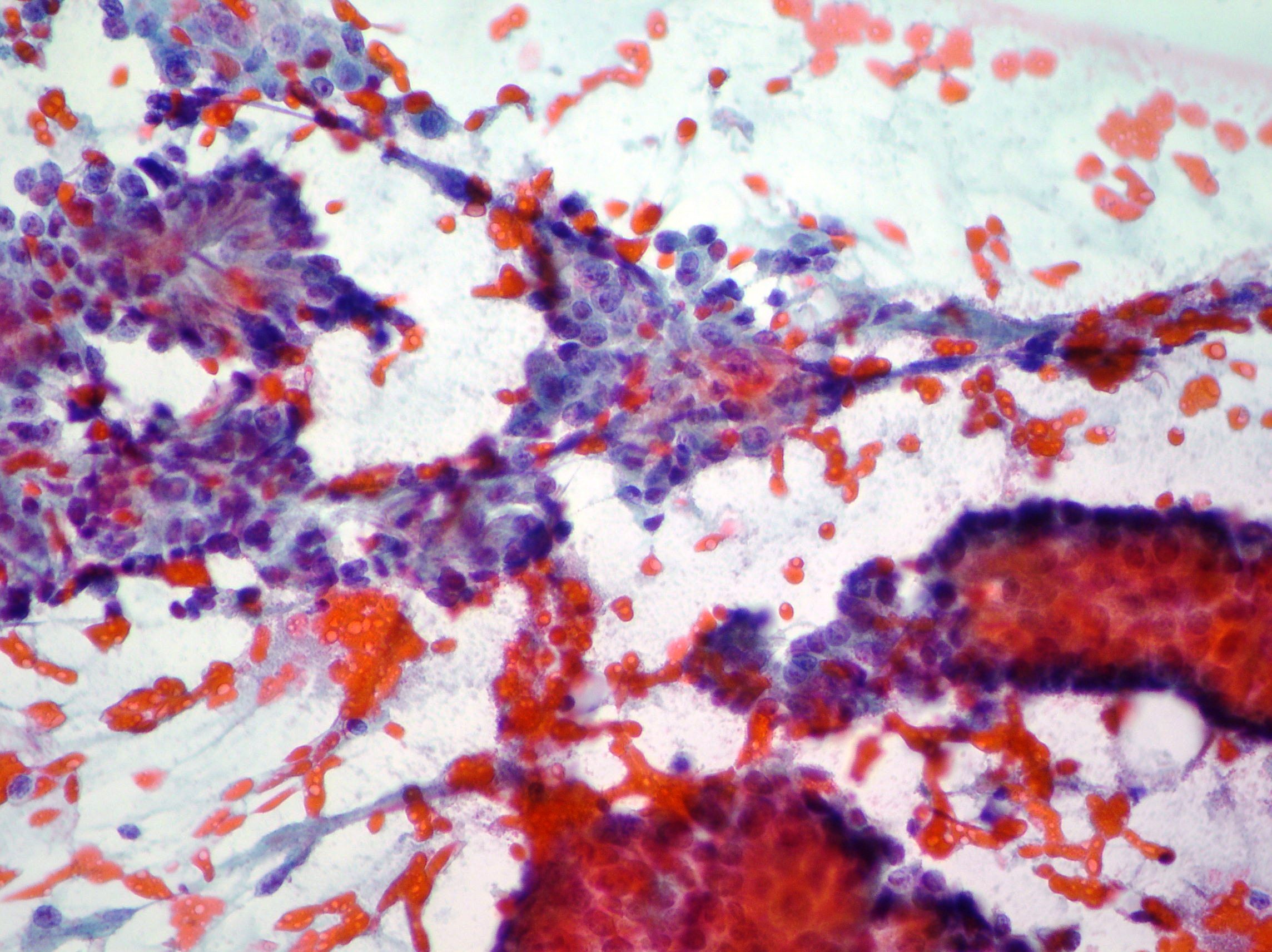
Mucinous pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Malignant epithelium showing pleomorphism, irregular nuclei and cytoplasmatic vacuolization suggestive of mucinous pancreatic adenocarcinoma. (Papanicolaou, x400)
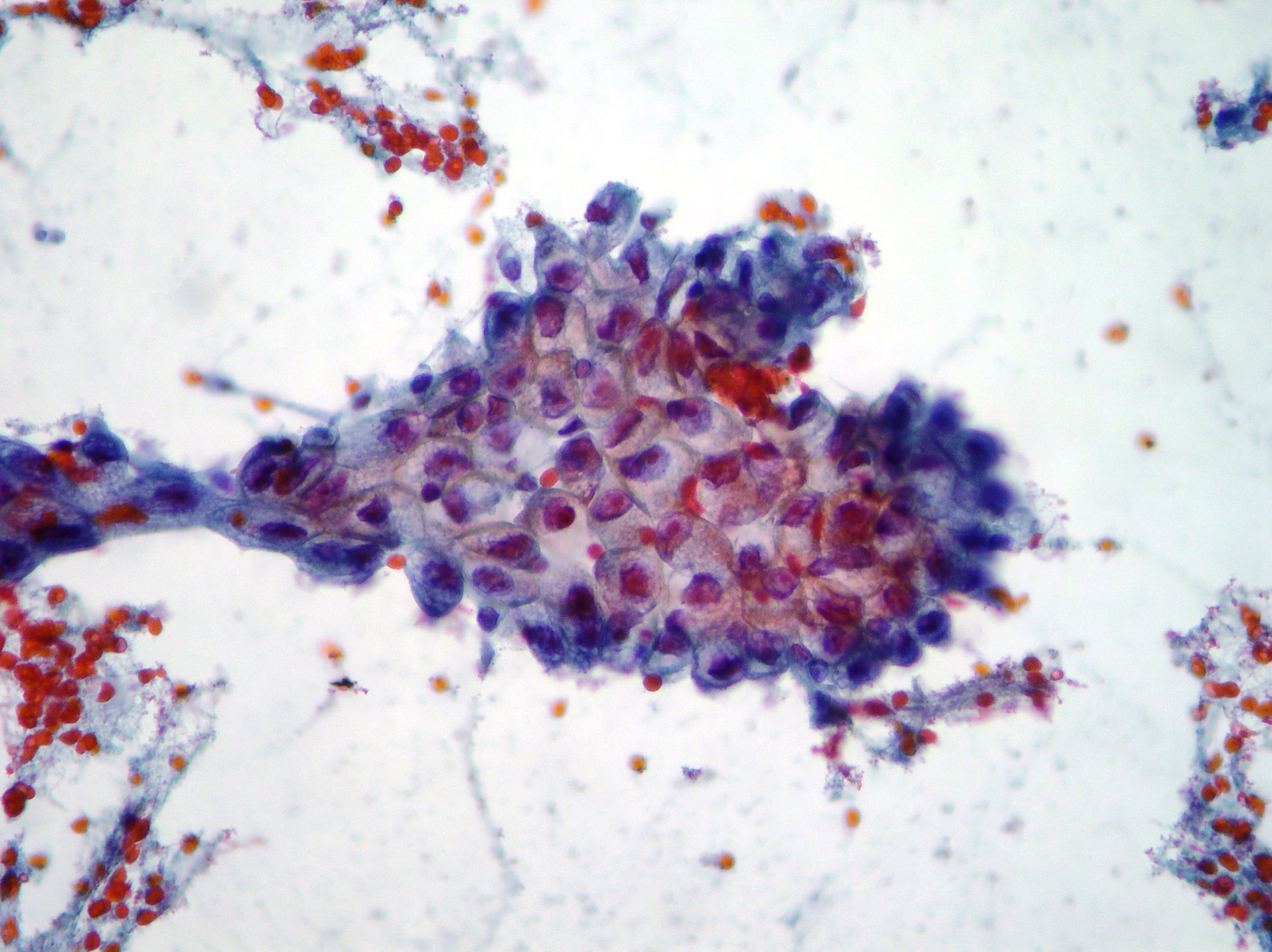
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Malignant epithelium representative of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Necrotic debris in the background. (Papanicolaou, x200)
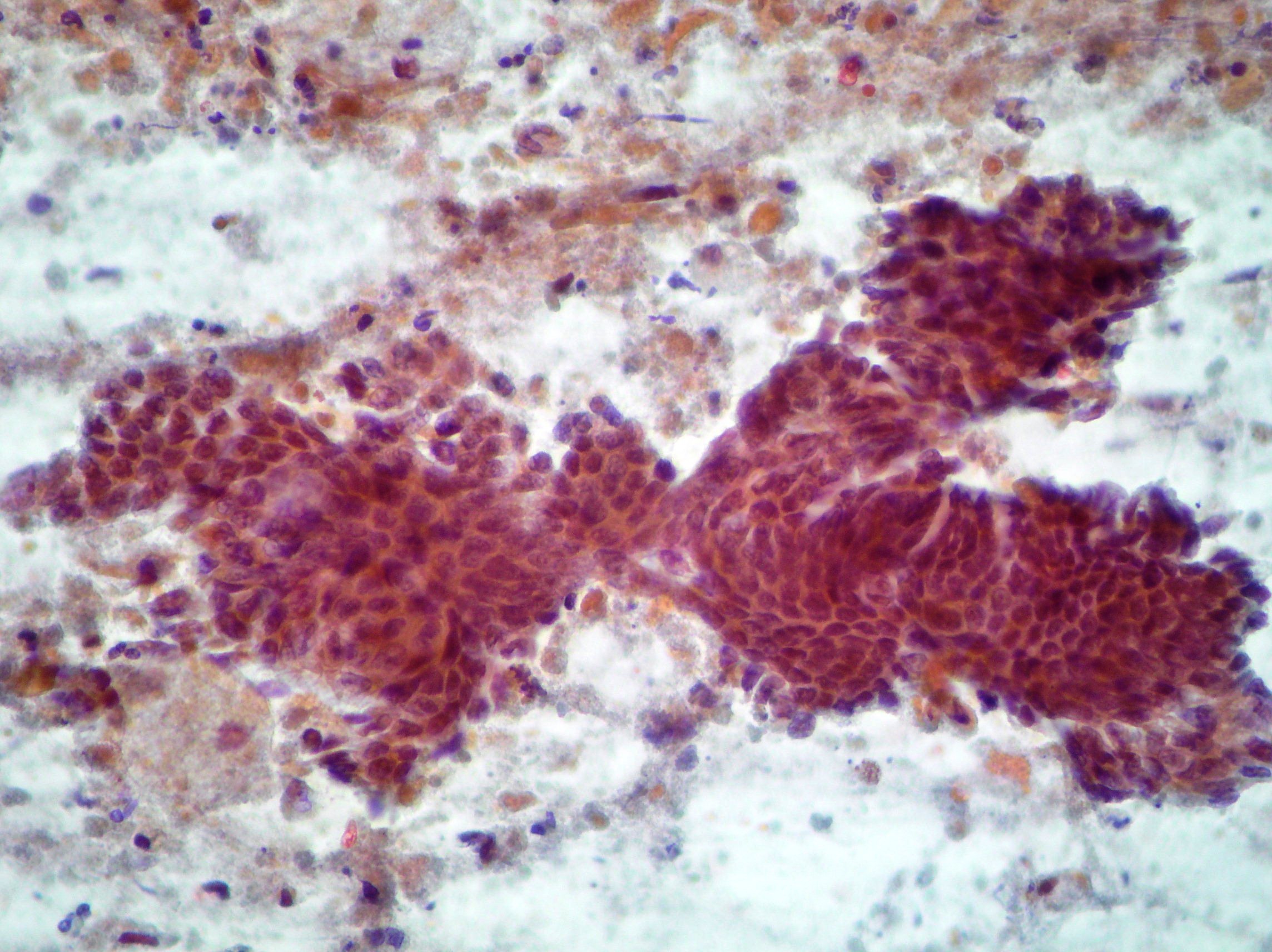
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Moderately differentiated pancreatic adenocarcinoma showing a cohesive cluster with acinar arrangements. (Papanicolaou, x400)
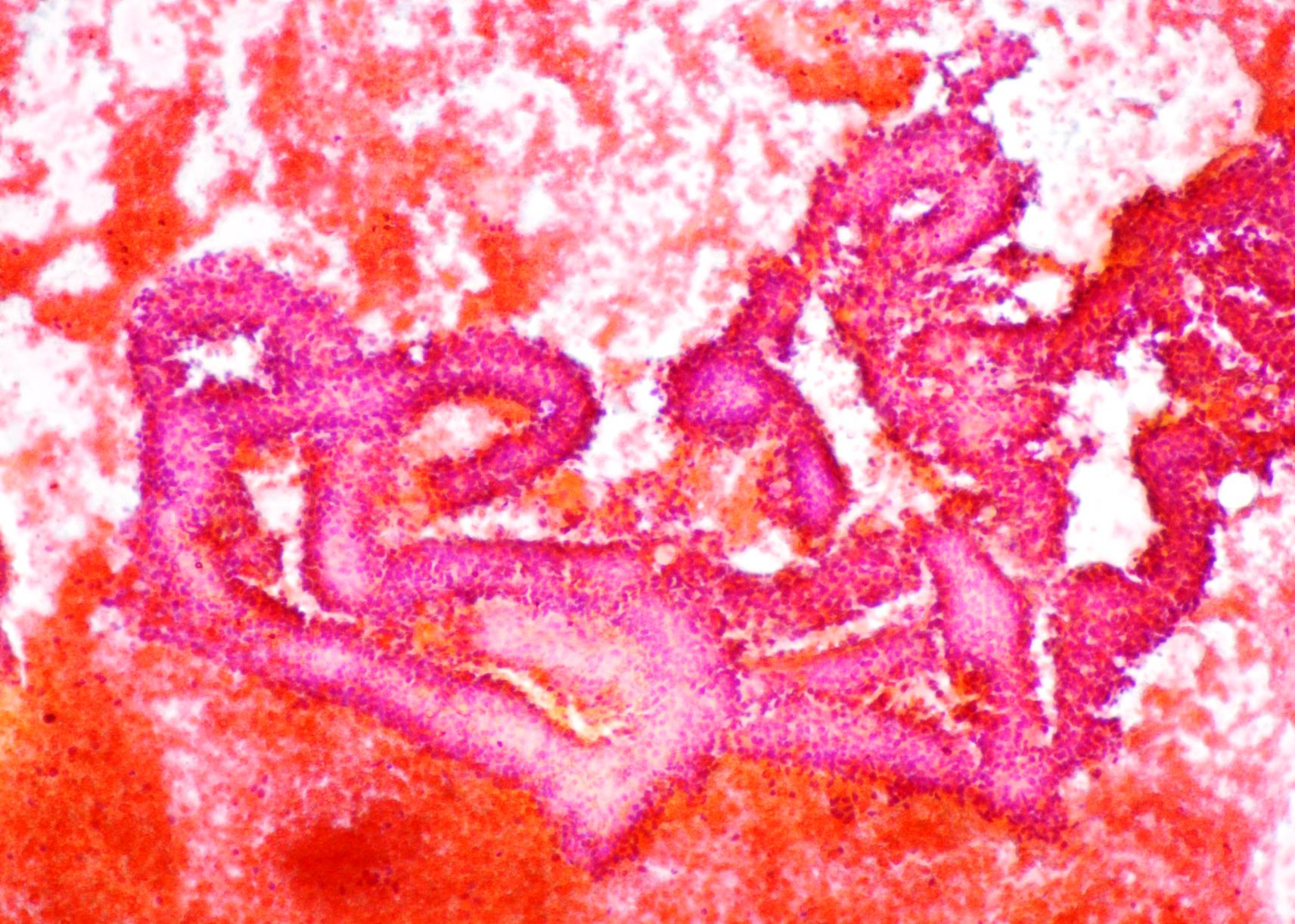
Pancreatic tubulo-papillary neoplasm
Pancreatic tubulo-papillary neoplasm fragment showing small tumor cells and discontinuous outer border sometimes scattered in the background. (Papanicolaou, x200, x100)
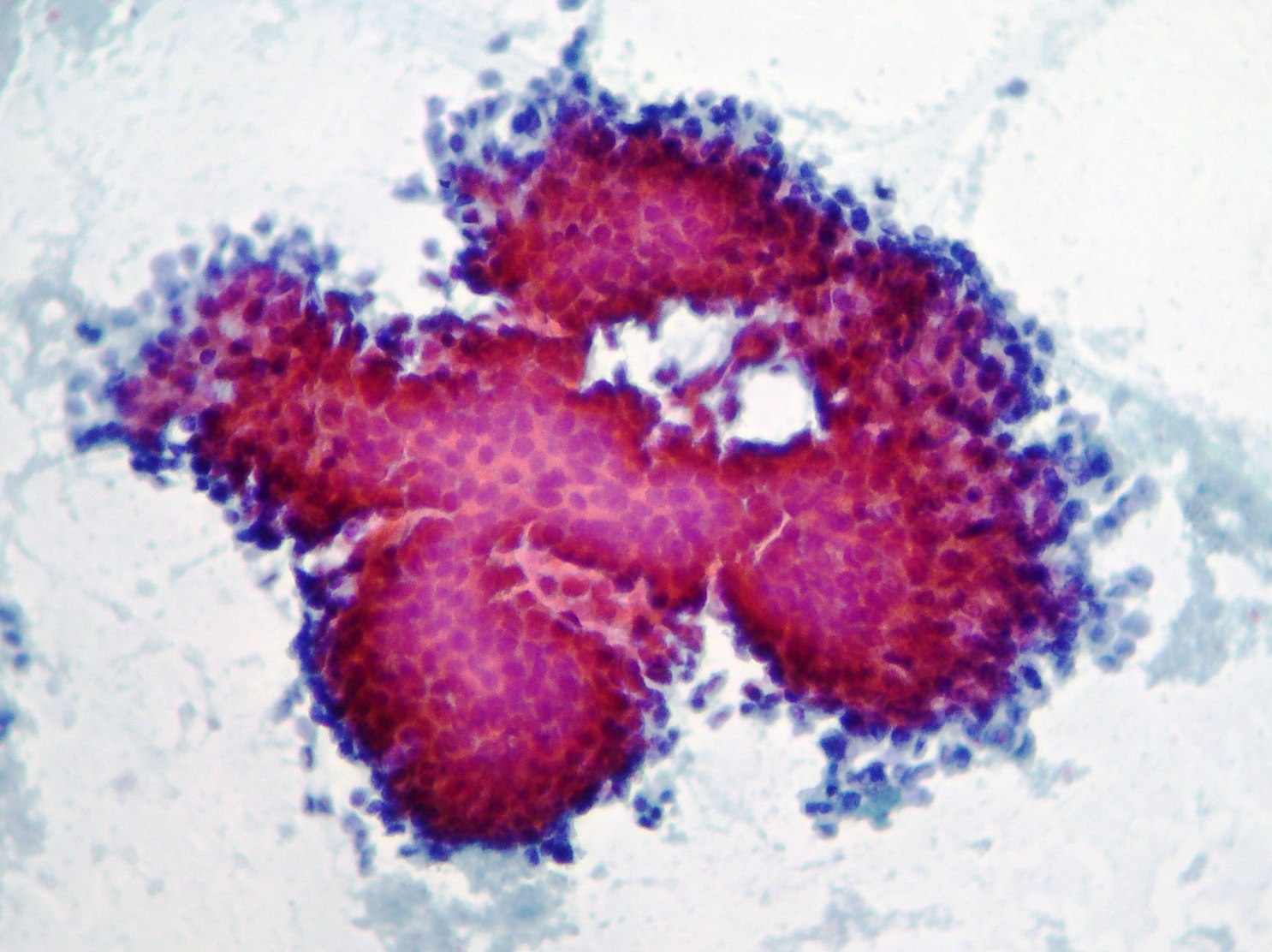
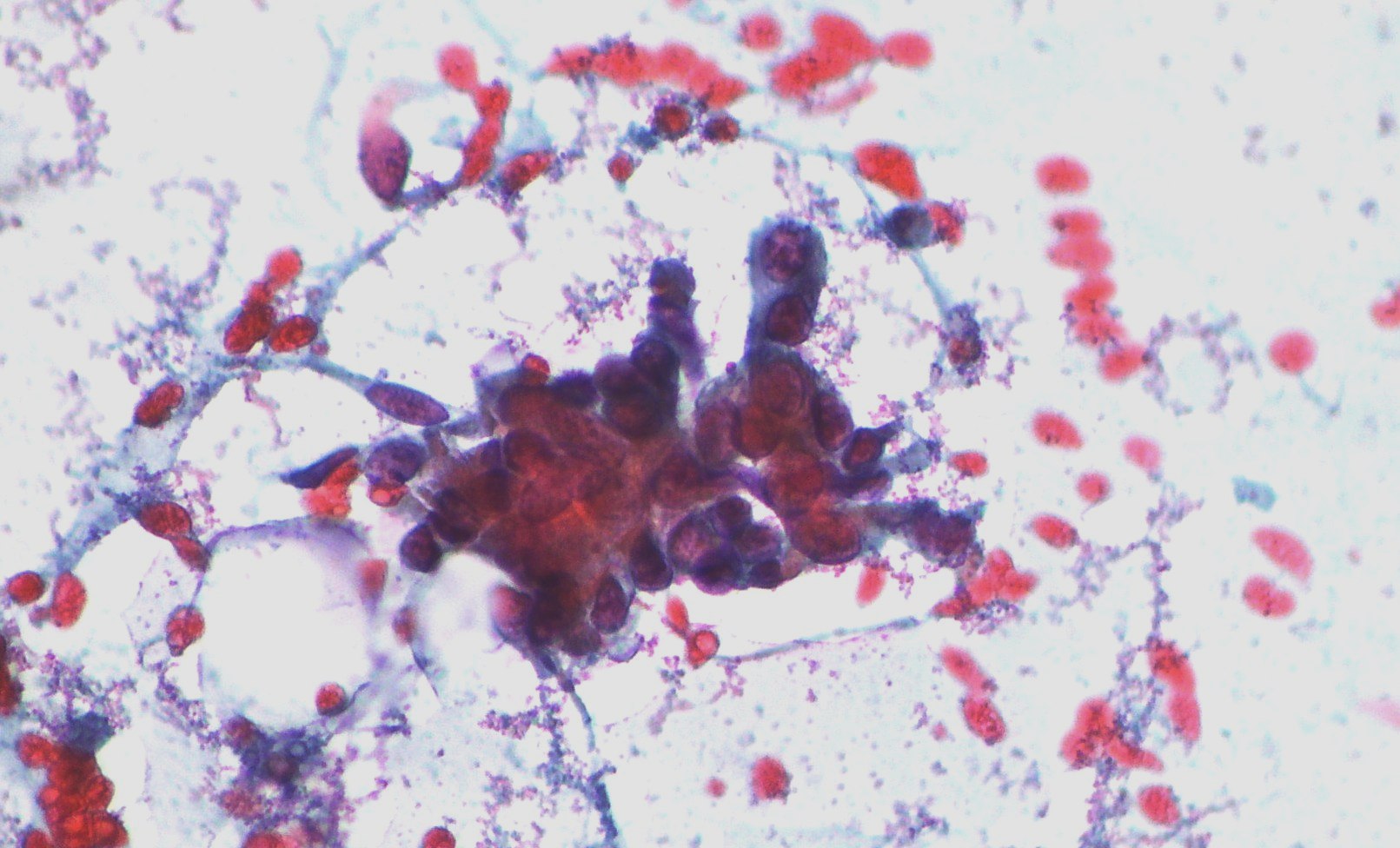
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Dispersed population and little aggregates of small cells with round nuclei, moderate anisokaryosis and fragile cytoplasm . CD 56 neuroendocrine immunocytochemistry marker showing cytoplasmatic positivity confirming the cytomorphology diagnoses.(Papanicolaou, x2oo)
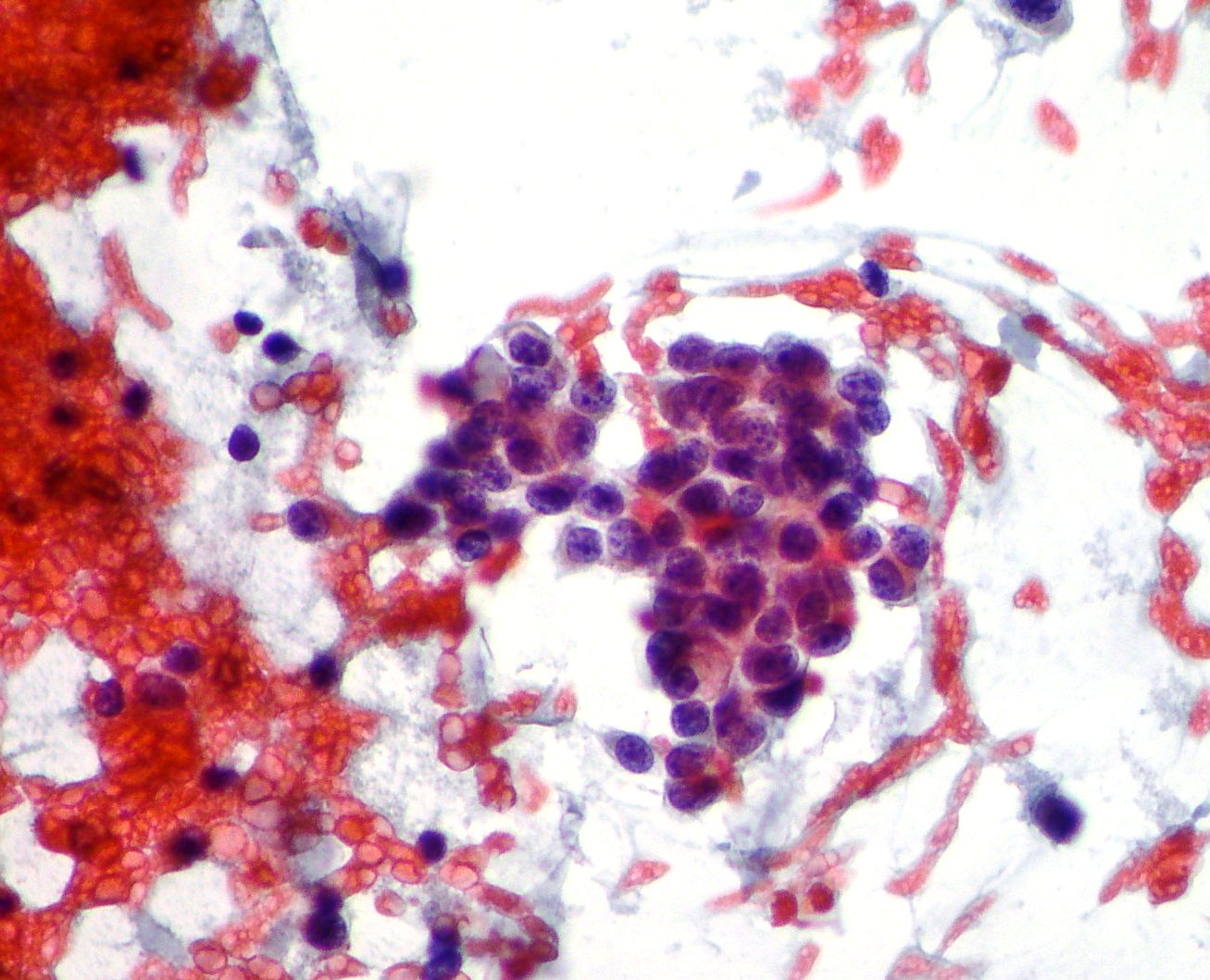
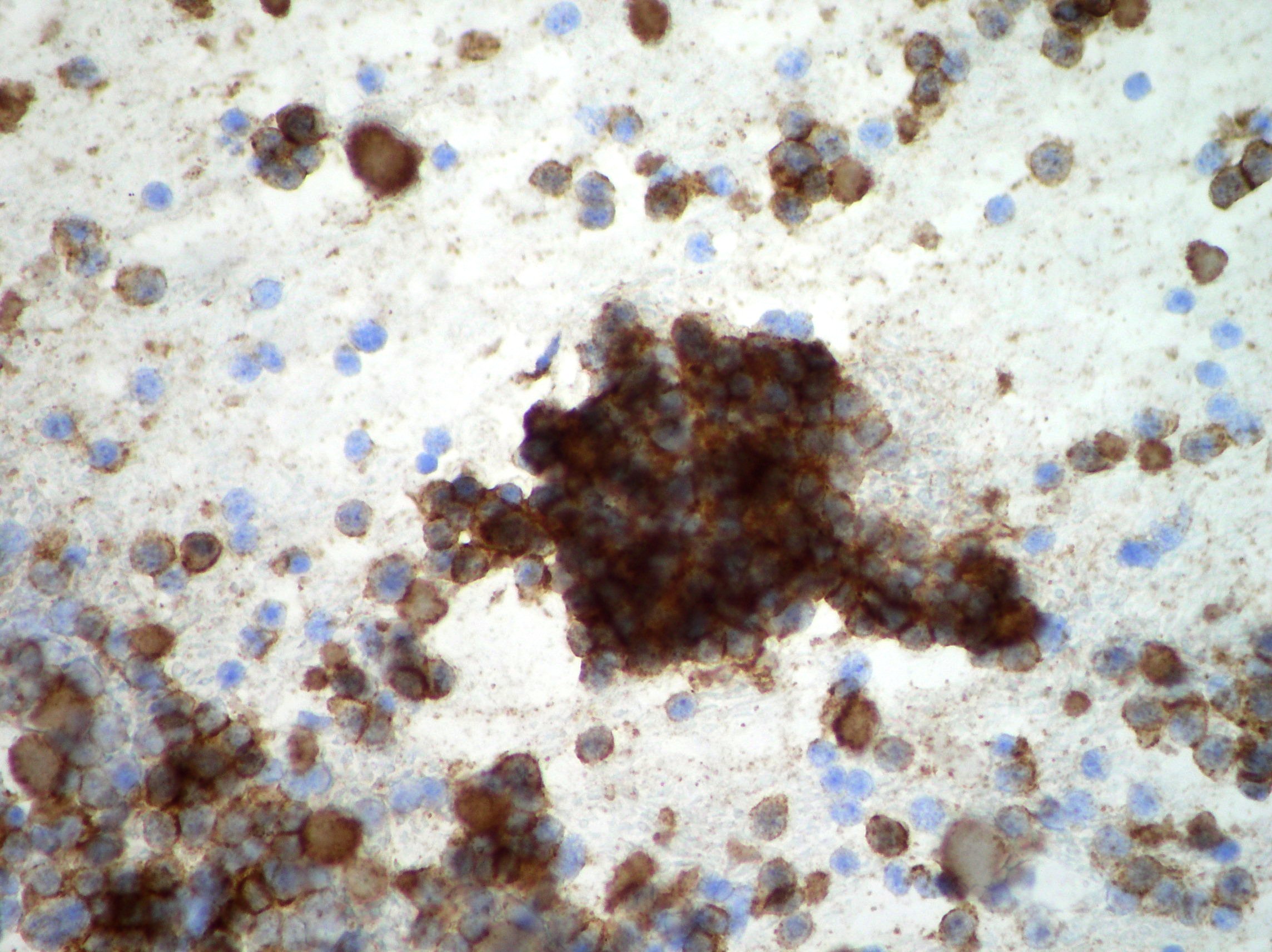
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
A group of malignant cells showing coarse chromatin and variations in nuclear size and shape suggestive of moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma. (Papanicolaou, x400)
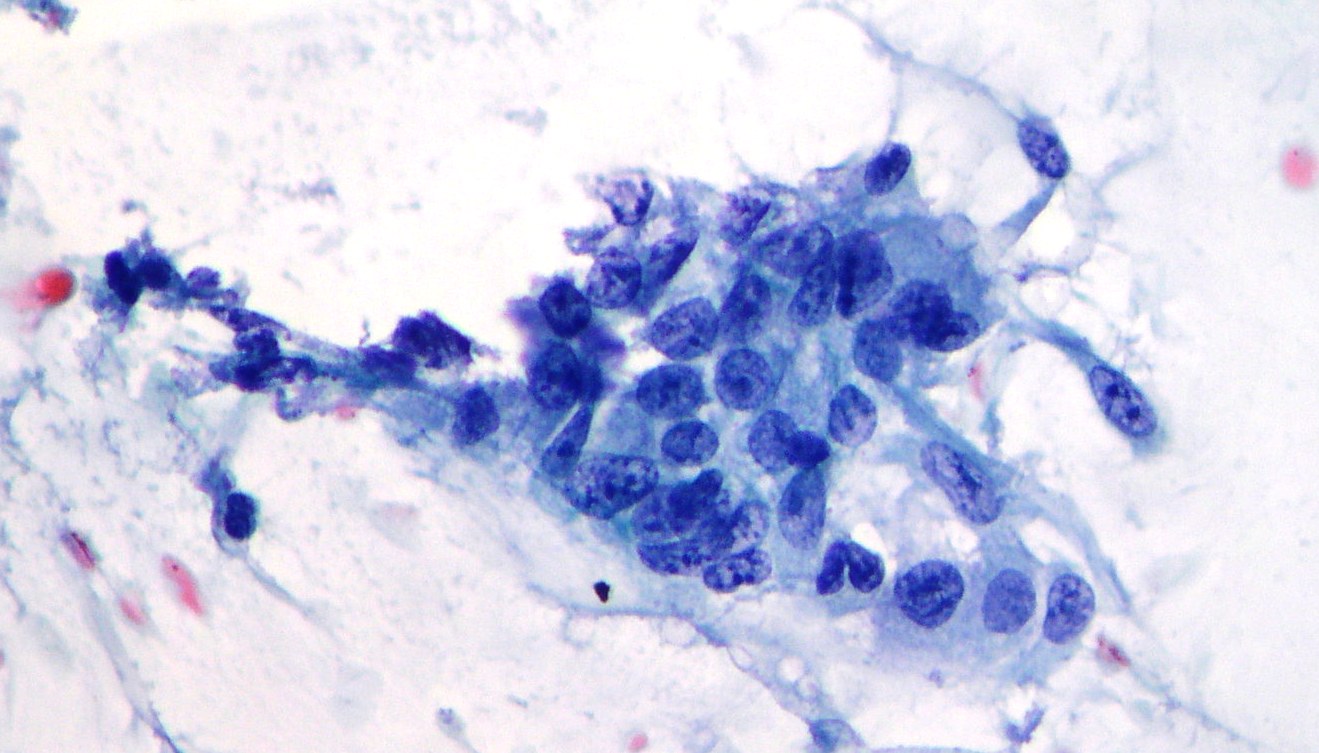
A monolayer sheet of ductal epithelium during pancreatic EUS-FNA procedure
A monolayer sheet of ductal epithelium with honeycomb cell borders and slight variation in nuclear sizes and chromatin can be aspirated during pancreatic EUS-FNA. Morphology is suggestive of duodenal cells contamination. (Papanicolaou, x200)